Industrial Automation, Consulting, News, Solutions
What is Robotic Welding? 7 Most Common Robotic Welding Processes
Robotic welding is a key automation process that helps modern industry enhance precision, improve occupational safety, and optimize production time. It is the most effective solution when applied to high-volume, repetitive welding tasks.
This article delves into the definition, structure, operating principles, and details of the 7 most common robotic welding processes in use today.
What is Robotic Welding?

Concept of Welding Robots in Industry
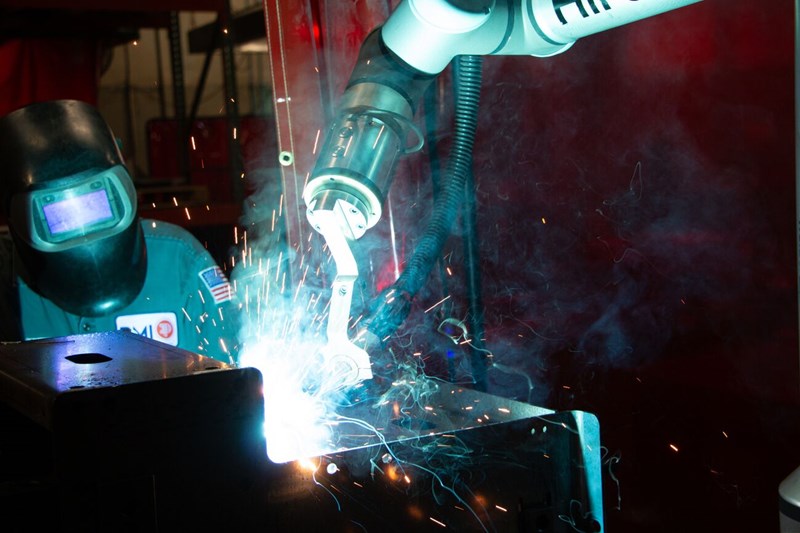
Robotic welding is the technique of welding automation, carried out by a type of dedicated industrial machine called a welding robot. These welding robots are often fixed in place and programmed to repeatedly execute a specific welding task.
An industrial robot is a programmable, controlled device capable of moving materials, parts, tools, or specialized equipment through programmed motions for tasks such as material handling, assembly, transportation, machine loading/unloading, and many other manufacturing applications. Industrial robots are commonly used in assembly lines or wherever materials need to be processed.
Welding robots were first introduced in the industry in the 1960s. In most cases, they are used for resistance welding and arc welding in heavy industries, particularly in automotive manufacturing.
Welding robots can operate in several ways: based on pre-programmed positions, using machine vision, or a combination of both. However, the most significant benefits offered by robotic welding technology are increased precision, repeatability, and production capacity.
How Does a Welding Robot Work?
The term ‘robot’ is often synonymous with ‘automation.’ Specifically, a welding robot is designed with an arm capable of flexible, three-dimensional movement to join metals together. A wire feeder supplies the welding wire to the robot, and a high-temperature welding torch is mounted at the end of the arm to melt the metal during the process.
Trained technicians are responsible for operating and maintaining the welding robot. They use a control box (or teach pendant) to program and adjust the robot’s operating sequence, and a separate control panel to initiate the welding process.
The tool at the end of the robot arm heats up to melt and connect the metal parts. When filler metal is needed, the wire feeder supplies more wire to the arm and the welding torch. Before starting the next weld, the arm moves the torch to a cleaning station to remove metal spatter, preventing blockages. Additionally, the robot is equipped with an arc shield to prevent high heat and oxygen from direct exposure, ensuring the safety of the operator and the surrounding area.
Benefits of Using Welding Robots
Integrating industrial welding robots provides outstanding advantages for manufacturers:
- Increased Productivity (Tăng năng suất): Robots work continuously 24/7 at a consistent speed, without fatigue or error, which shortens production cycles and increases output.
- High Accuracy (Độ chính xác cao): Welding robots have the ability to repeat movements with absolute precision, ensuring every weld is of consistent quality, minimizing spatter and material deformation.
- Reduced Labor Costs (Giảm chi phí nhân công): Optimization of human resources allows one skilled technician to supervise multiple automated welding stations simultaneously, rather than requiring many manual welders.
- Improved Weld Quality Consistency (Tăng tính ổn định chất lượng mối hàn): Weld quality is not dependent on the welder’s skill but is strictly controlled by the programmed sequence, ensuring lasting quality over time.
- Enhanced Occupational Safety (Đảm bảo an toàn lao động): Robots handle dangerous tasks, exposure to high temperatures, electric arcs, and toxic fumes, thereby protecting the health and safety of workers.
Structure of an Industrial Welding Robot
A complete robotic welding system consists of several cooperating components:
The Robotic Arm (Manipulator)
This is the main mechanical part, usually designed with 6 axes (6 Degrees of Freedom – DOF) to simulate human arm flexibility, allowing the torch to reach every complex position and angle on the workpiece.
Welding Robot Controller (Controller)
This is the brain of the system, containing control circuits and programming software. It receives and processes the welding program, coordinates the movement of the robot axes, and controls peripherals like the power source and wire feeder.
Welding Power Source & Equipment
Provides the necessary energy for the welding process (current, voltage) and auxiliary equipment such as the wire feeder, ensuring continuous and stable supply of filler material.
Welding Torch / Nozzle (Mỏ hàn / Béc hàn robot)
This is the tool attached to the end of the robotic arm, where the arc or laser beam is generated. It is specially designed to withstand high temperatures and possess the necessary mechanical durability for repetitive movements.
Sensors
Includes laser sensors, vision sensors, or force sensors. These sensors help the robot accurately determine the workpiece’s position, track the weld seam in real-time, and adjust movements to compensate for material changes or deviations.
Programming & Operating Software (Phần mềm lập trình & vận hành)
Includes the Teach Pendant (handheld controller) or Offline Programming software. This is the tool for technicians to set up, edit, and manage weld paths, speed, and other technical parameters.
Operating Principles of Welding Robots
The operating principle of a welding robot is based on a combination of precise mechanics, electronic control, and automated programming.
6-Axis Movement Mechanism
Most industrial welding robots are 6-axis type, allowing them to move with 6 degrees of freedom:
- Base Rotation.
- Shoulder Swivel.
- Elbow Swivel.
- Wrist Pitch.
- Wrist Yaw.
- Tool Roll.
This mechanism ensures the robot can accurately position the welding torch and maintain the optimal welding angle throughout the process.
Control and Programming Principle
The robot operates based on commands stored in the controller. Technicians use the Teach Pendant to guide the robot through waypoints, recording the position, speed, and welding parameters for each point.
After programming, the controller uses interpolation algorithms to calculate smooth and accurate movement trajectories between these points, ensuring consistent weld quality.
Automated Welding Cycle
An automated welding cycle typically follows this sequence:
- Preparation: The robot moves to the torch cleaning station to remove spatter and prepare the torch tip.
- Positioning: The robotic arm (possibly with vision sensors) moves the torch to the starting point of the weld.
- Welding: The power source is activated, and the wire feeder operates. The robot moves the torch along the programmed trajectory at a constant speed.
- Protection: Shielding gas is supplied to prevent high heat and oxygen exposure, protecting the weld.
- Completion: The weld is finished, the robot turns off the power source and moves to the next position or returns to the idle position.
7 Most Common Robotic Welding Processes
Industrial robots can adapt to various welding techniques. Here are the 7 most widely applied robotic welding processes.
1. Robotic MIG Welding (Metal Inert Gas)
MIG welding, or Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), uses inert gas (Argon, Helium) as shielding gas. This is a simple, fast process that creates a high volume of weld metal deposition.
- Applications: Welding carbon steel, stainless steel (inox), and aluminum. Popular in general manufacturing and metal structures.
- Advantages – Disadvantages: Advantages include high welding speed and easy automation. Disadvantages include higher shielding gas costs than MAG and less suitability for outdoor welding.
2. Robotic MAG / CO2 Welding (Metal Active Gas)
MAG welding uses active gas (usually CO2 or an Argon-CO2 mixture) as shielding gas.
- Difference from MIG: MAG uses active gas, which helps reduce the cost of shielding material (CO2 is cheaper than inert gas) and increases weld penetration.
- Applications in Steel Structures, Mechanical Engineering: Highly popular in structural steel welding, machine manufacturing, and heavy industry due to its economic efficiency and high weld strength.
3. Robotic TIG Welding (Tungsten Inert Gas)
TIG welding, or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode and inert gas shielding.
- Suitable for Stainless Steel, Aluminum: Chosen when extremely high weld quality and aesthetics are required. Often used for welding thin materials like stainless steel, aluminum, and special alloys.
4. Robotic Spot Welding (Hàn điểm)
A variation of resistance welding, joining two thin metal sheets together at a specific point by passing an electric current through two electrodes.
- Popular in the Automotive Industry: This is the foundational and most common technology for assembling car bodies and chassis, due to its ability to create fast, robust, and high-volume joints.
5. Robotic Arc Welding (Hàn hồ quang)
A general term for welding methods that use an electric arc to generate heat (including both MIG and TIG). The extremely high temperature (approx. 3,600°C or 6,500°F) melts the metal, creating a strong bond.
- Most Common Robotic Welding Type Today: Since MIG and MAG fall under arc welding, robotic arc welding is the most widely applied type in industrial production.
6. Robotic Plasma Welding
Similar to TIG but uses a plasma arc constricted through a nozzle.
- Applications in Heavy Industrial Manufacturing: Provides high temperatures and high energy density, allowing for faster welding speeds and deeper penetration than TIG. Offers maximum flexibility for the operator.
7. Robotic Laser Welding
Uses a high-intensity laser beam to generate heat and melt the metal.
- High Precision – Modern Trend: Ideal for joining small components that require extremely high precision, and applied in the production of jewelry, medical devices, and electronics.
Applications of Welding Robots in Industry
The development of robotic welding technology has created breakthroughs in many fields:
Automotive Industry – Motorcycle Components
This industry leads the way in applying spot and laser welding robots to assemble car bodies, chassis, and engine components. Robots ensure absolute consistency for millions of products.
Steel Structure – Mechanical Engineering
Uses robotic arc welding (MIG/MAG) to weld large structures, beams, columns, and heavy industrial machinery parts, where the welds must withstand heavy loads and have high durability.
Metal Furniture Manufacturing
Robotic welding automates repetitive welding stages on components like chair frames, tables, and beds, ensuring high aesthetics and reducing mass production costs.
Manufacturing of Industrial Equipment – Machinery
Applied to the assembly of complex parts for machine tools, agricultural machinery, and construction equipment, where robots can accurately access difficult positions.
Electrical – Electronics Industry
Mainly uses robotic laser and TIG welding to perform micro-welding on circuit boards, lithium-ion batteries, and sensitive electronic components.
5 Key Advantages of Robotic Welding for Manufacturers
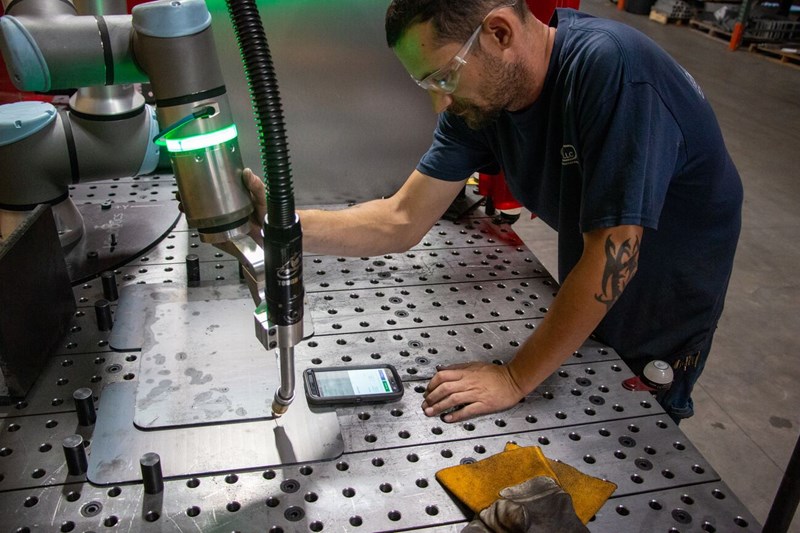

Robotic welding is increasingly common in fabrication shops and contract manufacturers due to the following benefits:
- Reduced Labor Effort (Giảm Công Sức Lao Động): Hiring, training, and retaining skilled welders is costly. With robotic welding, you can optimize human resources by only requiring one skilled welder to supervise multiple automated welding stations simultaneously.
- Increased Productivity (Tăng Năng Suất): Automation reduces personnel turnover by repeating high-quality welds in the exact position, limiting human error, and eliminating monotonous tasks.
- Reduced Waste (Giảm Lãng Phí): Robotic welding offers very high precision, helping to limit weld spatter and create cleaner, more aesthetic joints.
- Reduced Costs (Giảm Chi Phí): By using welding wire and filler materials more efficiently and economically, robotic welding helps reduce overall production costs.
- Time Savings (Tiết Kiệm Thời Gian): With stable installation processes and pre-set robot configurations, parts are processed faster, thereby increasing production capacity.
Comparing Robotic Welding with Manual Welding
While manual welding still plays a critical role in jobs requiring frequent technique changes, robotic welding demonstrates clear superiority in mass production:
Productivity
Robotic welding achieves 2 to 5 times higher productivity than manual welding, due to its ability to work continuously without rest and maintain optimal welding speed.
Weld Quality
Robotic weld quality is superior in terms of consistency, accuracy, and penetration compared to manual welding. Robots eliminate errors due to human factors such as fatigue or technical mistakes.
Operating Costs
Initially, the investment cost for robots is high. However, in the long run, robots significantly reduce labor costs, minimize waste of welding materials (wire, shielding gas) due to efficient use, and reduce costs from defects.
Occupational Safety
Robotic welding completely eliminates the risk of exposure to the arc, UV/IR radiation, high temperatures, and toxic welding fumes, creating a safer working environment for employees.
The Future of Robotic Welding
Currently, robotic welding is only applied in a small fraction of construction projects. However, with technological advancements, this trend is set to change. Future innovations will create more interactive welding robots, such as:
1. Mind-Controlled Welding Robots
Currently, to operate a welding robot, the operator must pre-program the sequence. In the future, operators may only need to “think” about the work to be done instead of manipulating a computer or control device. Researchers have developed a headset capable of converting brain signals into movements of the robotic welding arm. If applied in practice, this technology could significantly reduce the training time for manual welders transitioning to robot operation. Instead of computer programming, technicians would simply wear the headset and review the blueprint to guide the robot to weld correctly. However, this technology may take a long time to become widely accessible.
2. Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Prototypes of collaborative robots have been developed and put into trial use. These robots are designed to be user-friendly and easy to interact with humans. Equipped with sensors, they can collect data and respond flexibly to changes in the working environment. Previously, industrial robots required pre-programming to perform large-scale tasks. However, these devices were often bulky, expensive, and unsuitable for small businesses. To overcome this, engineers have developed more durable collaborative robots capable of working safely alongside humans in a production environment. Collaborative robots can assist manual welders directly in traditional welding zones.
How to Choose the Right Welding Robot for Your Business
To select the appropriate industrial welding robot, businesses need to carefully consider the following factors:
Selection by Welding Material
- Carbon Steel/Structural Steel: Prioritize MAG/CO2 welding robots for efficiency and low cost.
- Stainless Steel, Aluminum, Titanium: Prioritize TIG or laser welding robots to achieve high, clean, and aesthetic weld quality.
- Plastics or Thin/Sensitive Metals: Consider laser welding or spot welding (for thin metal sheets).
Selection by Workpiece Thickness
- Thick Workpieces (over 6mm): MAG/MIG (arc) welding robots with high current intensity to ensure deep penetration.
- Thin Workpieces (under 3mm): TIG or laser welding robots, which require high temperature control and precision.
Selection by Weld Type
- Straight, Long, Repetitive Welds: Any 6-axis welding robot is suitable.
- High-Volume Spot Welds: Dedicated spot welding robots (common in automotive).
- Complex, Multi-angle Welds: Requires a 6-axis robot with a large reach and the use of advanced controllers/vision sensors.
Should you choose Japanese, European, or Chinese robots?
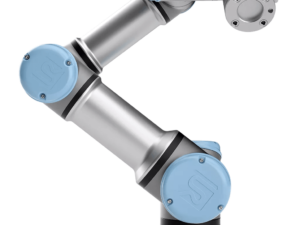
- Japanese/European Robots (e.g., Universal Robots): Known for durability, high repeatability, and advanced technology (like collaborative robots). Suitable for industries demanding strict quality standards (automotive, aerospace).
- Chinese Robots: Offer a cost advantage. Suitable for simple applications that do not require absolute precision, or for businesses with limited budgets.
Conclusion
Universal Robots (UR) is a world-leading manufacturer of Collaborative Robots (Cobots), known for their user-friendly design, flexibility, and high safety. These advantages make UR an ideal choice for businesses looking to implement or expand their robotic welding capabilities, regardless of size or previous automation experience.
Unlike traditional industrial robots that require complex programming and long setup times, Universal Robots’ cobots are designed to be easy to use, flexible, and efficient. These robots can work alongside humans, optimizing productivity without compromising quality. Key benefits include:
- Easy Programming: Intuitive interface allows for quick setup and reprogramming.
- Compact & Flexible Design: Suitable for both small- and large-scale welding applications.
- High Precision: Ensures consistent weld quality with minimal error.
- Enhanced Safety: Built-in safety features allow for safe collaboration with humans.
- Cost Savings: Reduces operating costs by optimizing material usage and minimizing waste.
Applications of Universal Robots in Welding
Universal Robots’ collaborative welding systems are widely used in industrial sectors such as:
- Automotive Manufacturing – Ensuring precise and consistent welds for vehicle parts.
- Metal Fabrication – Handling complex welding tasks with high accuracy.
- Aerospace Industry – Meeting strict quality standards for welding.
- Shipbuilding & Heavy Industrial Machinery – Automating repetitive, high-volume welding processes.
With Universal Robots, manufacturers can optimize their welding processes, reduce downtime, and achieve superior precision. As automation continues to evolve, collaborative robotic welding is the future of modern industrial manufacturing.
Explore Universal Robots's Products
Servo Dynamics Engineering: Authorized Distributor of Universal Robots in Vietnam
As the authorized distributor of Universal Robots in Vietnam, Servo Dynamics provides cutting-edge collaborative robot (cobot) solutions to enhance automation in manufacturing. With extensive expertise in robotic welding, assembly, material handling, and more, we help businesses integrate UR cobots seamlessly into their operations.
Our team offers professional consultation, technical support, and training, ensuring that companies maximize efficiency, safety, and productivity with flexible and user-friendly UR cobots. Partner with Servo Dynamics to unlock the full potential of robotic automation in Vietnam!
Learn More

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt