Consulting, News
6-Axis Robot: Structure, Working Principle, and Applications
This article will help you explore 6-axis robots – one of the most flexible and popular types of industrial robotic arms today. We will dive into the definition, a detailed overview of the structure of a 6-axis robot, the working principle of a 6-axis robot based on 6 Degrees of Freedom (6 DOF), as well as key applications and criteria for choosing the right robot.
What is a robot axis?
In the context of robotics, an axis can be understood as a Degree of Freedom (DOF). If a robot has 3 degrees of freedom, it can move along the X-Y-Z axes. However, it cannot tilt or rotate. When the number of axes (DOF) increases, the robot can reach more positions within its workspace.
Note that robots are usually purchased with a fixed number of axes, and it is almost impossible to add axes later. One way to determine the number of DOF of a robot is to count the number of motors. However, this can be difficult because the motors are often integrated inside the robot body. In general, the more axes a robot has, the more flexible it becomes. If you need the robot to perform a complex task, you will need a robot with more axes.
Classification of robots by number of axes
Below is a description of common types of robots categorized by their number of DOF. Note that depending on the manufacturer, a certain type of robot may have a different number of axes, so consider this information as a general guideline.
3-axis robots
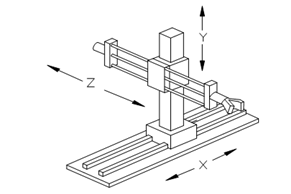
3-axis robots – also known as Cartesian or SCARA robots – can be compared to 3-axis CNC machines or 3D printers. They allow the tool to move along three axes thanks to three different motors.
These robots are often used for simple pick-and-place operations, where parts are placed in the same orientation and at a fixed position. For example, if a robot grips a part in a certain orientation, it has to move in that same orientation because the tool cannot rotate.
A typical example of a 3-axis robot is a crane.
4-axis robots
4-axis robots can rotate the part around a fourth axis while still moving along the X-Y-Z axes. SCARA, Delta, and some traditional robots fall into this category.
A 4-axis robot typically has 4 motors, where the fourth axis is used to rotate the tool. For example, if a part is on a conveyor belt, the robot will need to locate the part (X-Y axes), move down to the correct height (Z axis), and finally rotate the tool to match the orientation of the part.
5-axis robots
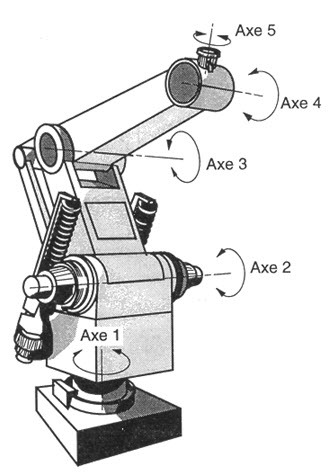
At this level, traditional industrial robots begin to appear. Many industrial robots have 5 axes, allowing them to move along the X-Y-Z axes and rotate the tool around two other axes.
In other words, the robot can rotate around the Z axis and Y axis, but not around the X axis. This means the robot does not yet have full freedom and there are still positions it cannot reach.
An example of a 5-axis robot is a 5-axis CNC machine, where the tool can move along the X-Y-Z axes, the worktable rotates around the Z axis (forming the 4th axis), and the worktable can tilt around another axis (forming the 5th axis).
6-axis robots
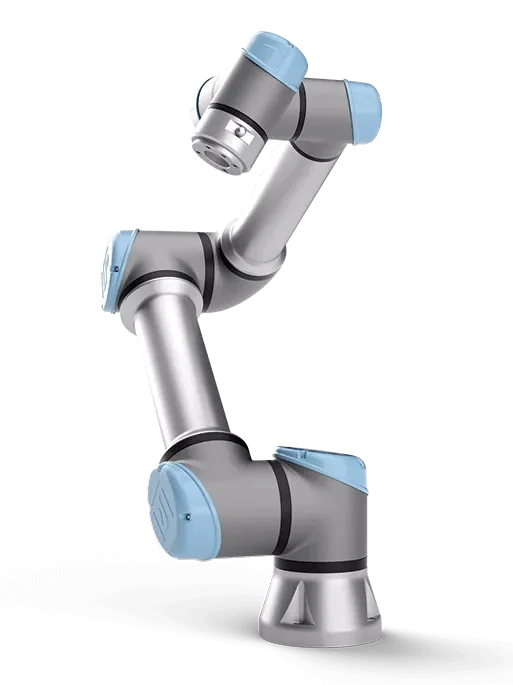
6-axis robots have the minimum full degrees of freedom: they can move along the X-Y-Z axes and rotate around each of these axes.
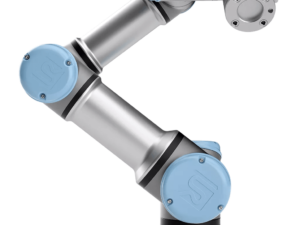
The difference between a 5-axis and a 6-axis robot is that the 4th and 5th axes of the 6-axis robot can rotate around another axis, giving it greater flexibility. A typical example of a 6-axis robot is a Universal Robot.
7-axis robots
If a 6-axis robot can already reach every position in space, why do we need a 7-axis robot?
The 7th axis allows the robot to reach the same position with multiple different joint configurations. This helps avoid singularities and enables the robot to move around obstacles by adjusting its arm more flexibly than a 6-axis robot.
An example of a 7-axis robot is the Motoman SDA series. These robots are also called “redundant robots” because they have one more axis than the minimum required.
12- and 13-axis robots
These are essentially two 6-axis robots combined to form a dual-arm robot. If the base of the robot can rotate around itself, it will have an additional axis, bringing the total to 13.
However, in 3D space, these robots cannot extend their working range beyond that of 6- or 7-axis robots, because they still operate within the same three spatial dimensions that humans can perceive.
What is a 6-axis robot?
A 6-axis robot is the most widely used type of industrial robot today. It is designed to mimic the human arm, offering outstanding flexibility in manufacturing environments.
Definition of a 6-axis robot
6-axis robots (6-axis robots) are articulated robotic arms that possess six degrees of freedom (6 Degrees of Freedom – 6 DOF). These six rotary joints allow the robot to move and orient the end-of-arm tooling (EOAT) to almost any position and angle within its working envelope.
The most prominent feature of a 6-axis robot is its ability to achieve full freedom of movement in 3D space, meaning it can perform 3 translational motions (X, Y, Z) and 3 rotational motions (Pitch, Yaw, Roll) independently.
Key differences between 6-axis robots and 3–4–5-axis robots
The core difference lies in the number of degrees of freedom (DOF), which determines the flexibility and complexity of the tasks the robot can perform.
| Robot Type | Number of DOF | Basic Motion | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-axis | 3 | Linear motion in X, Y, Z | Simple pick and place, 3-axis CNC machines. |
| 4-axis | 4 | Linear X, Y, Z + 1 rotation (usually Yaw) | SCARA, Delta robots. Tasks requiring simple orientation. |
| 5-axis | 5 | Linear X, Y, Z + 2 rotations (often lacking rotation around the main axis) | 5-axis CNC machines, robots that need to tilt the workpiece. |
| 6-axis | 6 | Linear X, Y, Z + 3 rotations (Pitch, Yaw, Roll) | Welding, complex assembly, painting, surface processing. Maximum flexibility. |
| 7-axis | 7 (Redundant) | 6 basic DOF + 1 additional axis | Helps the robot avoid obstacles, avoid singularities, and increase its working envelope. |
Why are 6-axis robots widely used in manufacturing?
6-axis robots dominate modern production lines thanks to:
- High flexibility: Their ability to closely mimic human arm motion allows them to perform complex, multi-dimensional tasks.
- Multi-tasking: A single robot can be easily switched between applications such as welding, assembly, or painting simply by changing the end-of-arm tool and program.
- Accuracy and repeatability: They achieve high accuracy and repeatability in trajectory execution, which is critical for high-quality processes.
Structure of an industrial 6-axis robot
To fully understand how a 6-axis robot works, we need to grasp the basic structure of an industrial 6-axis robot, including the mechanical system and the control system.
6 joints / 6 axes of motion (Joint 1 → Joint 6)
These are rotary joints that define the 6 degrees of freedom of the robot:
| Joint | Name | Function | Motion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Joint 1 (J1) | Base axis | Rotates the entire robot arm around the vertical axis (Yaw). | Determines horizontal position. |
| Joint 2 (J2) | Shoulder axis | Moves the arm up and down (Pitch). | Determines height. |
| Joint 3 (J3) | Elbow axis | Bends/extends the arm (Pitch). | Determines reach (distance). |
| Joint 4 (J4) | Wrist Roll axis | Rotates the wrist. | Adjusts the rotation angle of the tool. |
| Joint 5 (J5) | Wrist Pitch axis | Tilts the wrist up and down. | Adjusts the tilt angle of the tool. |
| Joint 6 (J6) | Wrist Yaw axis | Rotates the wrist around the vertical axis. | Adjusts the orientation of the tool. |
Robot Controller
The controller is the “brain” that manages all robot operations.
- Functions and role:
- Executes the programmed instructions.
- Controls the servo motors (position, speed, acceleration).
- Processes signals from sensors and peripheral devices.
- Performs coordinate transformations (for example: from Joint to Cartesian).
- Popular controller series: Each brand has its own controller, such as ABB IRC5, Yaskawa DX200, KUKA KRC4, Fanuc R-30iB Plus, etc.
Drive system – Servo motors – Encoders
- Servo Motors: These are AC electric motors used to generate motion for each joint. Servos allow precise control of speed and position.
- Gearboxes: Various types of gear reducers (often Harmonic Drive or Cycloidal) are used to increase torque and reduce speed, ensuring the robot can lift heavy loads and move smoothly.
- Encoders: These are position feedback devices attached to the motor or joint, enabling the controller to know the exact rotation angle of each axis.
Grippers / EOAT (End of Arm Tooling)
EOAT is the tool mounted on the last joint (J6), and it determines the robot’s main function:
- Pneumatic grippers: Use air pressure to grip or release objects.
- Electric grippers: Use electric motors, often allowing precise control of gripping force and position.
- MIG/TIG welding torches: Used for automated welding applications.
- Vacuum grippers: Use suction cups to lift flat materials such as glass, metal sheets, or packaging.
- Spray/dispensing nozzles, grinding/polishing tools, inspection sensors.
Control cabinet and peripheral connection system
This includes electronic devices such as power supplies, backup power units, and I/O modules (Input/Output) to connect the robot with conveyors, safety sensors, the main PLC of the factory, and other peripheral equipment.
Working principle of a 6-axis robot
A 6-axis robot operates based on the smooth coordination between mechanical components and complex control algorithms.
6-DOF motion mechanism
The 6 degrees of freedom allow the robot to move in 6 different ways, reaching any point within its working envelope at any orientation. This is achieved by adjusting the rotation angles of joints J1 to J6.
Coordinate systems (Joint – XYZ – Tool – User Frame)
Several coordinate systems are used to control the robot:
- Joint Frame: Describes the position using the rotation angle of each joint (for example: $J1 = 30^{\circ}, J2 = 45^{\circ}, \dots$).
- XYZ Frame (Cartesian/World coordinates): Describes the position of the Tool Center Point (TCP) in space using coordinates (X, Y, Z) and orientation angles (Rx, Ry, Rz) relative to the global origin.
- Tool Frame: Attached to the tool (EOAT), helping the programmer define motion from the tool’s point of view.
- User Frame: Attached to a fixed object or worktable, simplifying programming on inclined or offset objects.
Motion control: Interp, Path Control, Speed Control
- Interp (Interpolation): Algorithms that calculate the trajectory between two points A and B, ensuring smooth and accurate motion. Common interpolation types are Joint (fast motion, not a straight line), Linear (straight-line motion), and Circular (circular arc motion).
- Path Control: Ensures the robot follows the calculated path.
- Speed Control: Adjusts the overall movement speed and the speed of each joint.
Basic operating process of a 6-axis robot
- Programming: Defining the points and paths that the robot must follow.
- Setting points (TCP, Zeroing):
- TCP (Tool Center Point): Accurately determining the position of the tool center (the EOAT’s point of action). This is essential for precise robot motion.
- Zeroing: Resetting the home position of the joints.
- Test Run: Running the program at a low speed to check for collisions and path errors.
- Production: Running the program at optimal speed and integrating it into the production line.
Benefits of using 6-axis robots
Using 6-axis robots brings many significant benefits to businesses, especially in the context of modern, increasingly competitive manufacturing:
- Flexible and versatile: With multi-directional operation and smooth movement along 6 axes, the robot can perform many complex tasks such as assembly, welding, painting, and material handling over a wide working range, helping to optimize production processes.
- High accuracy: Advanced technology enables the robot to achieve excellent accuracy and repeatability, minimizing errors and ensuring consistent product quality.
- Easy integration into production lines: A user-friendly programming interface and high customizability make robots easy to integrate into modern automation systems, shortening deployment and commissioning time.
- Safe collaboration with humans: 6-axis robots, especially collaborative robot (cobot) series, are equipped with sensing technologies and safety designs to ensure safe interaction between robots and workers, enabling more flexible production setups.
- Cost savings and higher efficiency: By adopting automation with 6-axis robots, companies can reduce labor costs, increase productivity, and minimize production risks, thereby gaining a stronger competitive edge in the market.
Common types of 6-axis robots on the market
The 6-axis robot market is very diverse, with many leading global brands:
- Universal Robots 6-axis robots (UR): A pioneer in Collaborative Robots (Cobots). Features: Easy programming, safe collaboration with humans, suitable for light to medium payload tasks (from 3 kg to 16 kg).
- ABB 6-axis robots: A top brand offering a wide range of industrial robots with various payloads and reaches, well-known for IRB series and IRC5 controllers. Segment: Heavy-duty and high-speed industries.
- KUKA 6-axis robots: A German brand distinguished by high-payload robots with exceptional accuracy (such as the KR series). Segment: Automotive, casting, welding.
- Yaskawa (Motoman) 6-axis robots: Offers a wide product range, particularly strong in welding and material handling applications. Segment: High-speed, durable solutions.
- Fanuc 6-axis robots: Renowned for durability, reliability, and continuous operation in harsh environments. Segment: Automotive and metal industries.
- Mitsubishi/Kawasaki/Epson/Yamaha/Hiwin/Inovance 6-axis robots: Provide specialized solutions, often focusing on light payloads and high precision for electronics, assembly, and cost-effective applications.
Industrial applications of 6-axis robots
Thanks to their flexibility, 6-axis robots are found in almost every industry.
Automatic MIG/TIG welding
6-axis robots ensure stable, accurate welding speed and bead quality, especially for complex parts, helping increase productivity and reduce weld defects.
Material handling, packaging, palletizing
With good reach and load capacity, 6-axis robots are used to move goods and automatically stack products on pallets (palletizing), reducing manual labor and increasing warehouse handling speed.
Electronics assembly
The high accuracy and repeatability of 6-axis robots make them ideal for assembling small, complex components in the production of phones, computers, and other electronic devices.
Painting – adhesive dispensing – coating
Robots ensure uniform coating and stable spray rates, which is especially important in the automotive industry and high-end furniture production. J4, J5, and J6 play a key role in orienting the spray head.
CNC tending – pick & place
Robots perform pick operations from storage and place parts into CNC machines (machine tending), then remove the finished products. They are also used for surface processing tasks such as grinding and polishing.
Applications in automotive, electronics, and logistics industries
- Automotive: Body welding, engine assembly, painting.
- Electronics: PCB assembly, quality inspection (QC), labeling.
- Logistics: Sorting and stacking goods, parcel sorting.
Programming 6-axis robots
There are two main programming methods, along with brand-specific languages and required skills.
Online programming (Teach Pendant)
Using the teach pendant to move the robot to each desired point and record its coordinates. This method is intuitive and suitable for simple tasks and quick adjustments.
Offline programming (RobotStudio, RoboDK, Melfa Works…)
Using 3D simulation software on a computer to create programs before deploying them on the real robot. This method shortens installation time, optimizes paths, and helps avoid collisions in a virtual environment.
Brand-specific programming languages (ABB RAPID, KUKA KRL…)
Each manufacturer has its own programming language:
- ABB: RAPID
- KUKA: KRL (KUKA Robot Language)
- Fanuc: KAREL
- Universal Robots: Polyscope (graphical interface)
Skills required to operate 6-axis robots
- Basic knowledge of mechanics, electronics, and automation.
- Understanding of coordinate systems (Tool, User, World).
- Ability to read and write logical programs (Boolean logic, If/Else, For loops).
- Error handling and safe operation skills.
Advantages and limitations of 6-axis robots
Advantages
- Outstanding flexibility: With 6 degrees of freedom, they can perform nearly any task.
- High accuracy and repeatability: Ensures consistent product quality.
- Diverse payloads and reaches: Easy to find robots suitable for demands ranging from 3 kg to several hundred kg.
- High freedom of motion: Handle complex tasks requiring smooth, curved trajectories.
Limitations
- High cost: Initial investment is higher than that of simple 3–4-axis robots.
- Complex programming: Requires engineers with in-depth expertise in coordinate and trajectory calculations (except for cobot lines with user-friendly interfaces).
- Challenging maintenance: Without an in-house technical team or a professional supplier, maintenance and repairs can be costly.
Comparison between 6-axis robots and other robot types
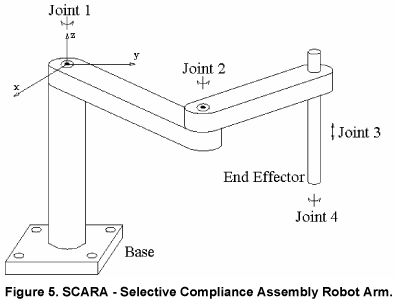
4-axis robots (SCARA)
SCARA (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm) has only 4 DOF and is mainly used for high-speed pick & place tasks on a horizontal plane. 6-axis robots are much more flexible because they can orient the tool at any angle.
Delta robots
Delta (Spider) robots are extremely fast and are specialized for ultra-lightweight pick & place tasks. Their working area is limited to a spherical/hemispherical region below the robot. 6-axis robots are more flexible in terms of workspace and payload.
Cartesian robots
Cartesian robots move along 3 linear axes (X, Y, Z). They are suitable for tasks within a box-shaped volume. 6-axis robots are preferred when curved motion, tilting, or operation in constrained spaces is required.
When should you use a 6-axis robot?
You should invest in a 6-axis robot when:
- The task requires the tool to tilt, rotate, or reach confined angles (for example: welding, painting, 3D assembly).
- You need the robot to perform multiple different tasks on the same production line (multi-purpose).
- You require very high accuracy in tool orientation.
How to choose the right 6-axis robot
Select by payload and reach
These are the two most important factors. The payload must be greater than the total weight of the EOAT and the heaviest workpiece. The reach must cover the entire working area.
Select by application (welding, pick & place, assembly…)
- Welding/Painting/Machining: Requires high repeatability and flexible wrist motion (good J4, J5, J6 performance).
- Pick & Place/Logistics: Prioritize wide reach and high speed.
- Assembly: Prioritize accuracy and safe collaboration, especially with cobots.
Select by brand – cost – technical support
- Brand: Major brands (UR, ABB, Fanuc, KUKA) ensure quality but come with higher costs.
- Cost: Balance between initial investment and total cost of ownership (TCO), including maintenance, operation, and training costs.
- Technical support: Very important in Vietnam. Choose a reputable supplier with a strong engineering team to ensure quick issue resolution.
Notes for first-time robot investment
- Proof of Concept (PoC): Always ask the supplier to perform tests on your real application before making an investment decision.
- Training: Ensure staff are properly trained in programming and safe operation.
- Safety: Integrate full safety features and sensors (for example: safety fences, emergency stop functions).
Why choose Universal Robots?
Universal Robots is committed to delivering flexible, safe, and easy-to-use 6-axis industrial robotic arm solutions to businesses of all sizes worldwide. We develop industrial collaborative robots to automate and streamline repetitive industrial processes. This approach allows production departments to reassign staff to more interesting work – helping them build skills in more challenging tasks and thereby increase their value to the company.
Popular Universal Robots series
- UR3e: With a payload of up to 3 kg, the UR3e is an ideal solution for precise, delicate tasks such as component assembly, quality inspection, and applications in confined workspaces.
- UR5e: With a maximum payload of 5 kg, the UR5e strikes a balance between compact size and wide reach, suitable for packaging, assembly, and light material handling tasks in modern production environments.
- UR10e: With a 10 kg payload, it offers a wide working envelope and high performance for applications requiring interaction with complex automated systems, from assembly to handling industrial parts.
- UR16e: The most powerful in the series with a payload of up to 16 kg, the UR16e is designed for heavy-duty applications, ensuring stable performance in harsh production environments and processes that demand both high precision and high load capacity.
Servo Dynamics Engineering: Authorized distributor of Universal Robots in Vietnam
Universal Robots is committed to delivering flexible, safe, and easy-to-use 6-axis industrial collaborative robot (cobot) solutions to businesses of all sizes. Highlighted UR robot series such as UR3e (3 kg), UR5e (5 kg), UR10e (10 kg) and UR16e (16 kg) are designed to automate repetitive processes, allowing staff to focus on higher-value tasks.
Servo Dynamics is proud to be the official distributor of Universal Robots in Vietnam. We are committed to providing high-quality collaborative robot solutions, along with dedicated consulting, installation, and technical support services to help customers fully unlock the potential of cobots in production.
Discover Universal Robots products
Read more

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt