Consulting, Industrial Automation, News, Solutions
Surge Protection Devices: Types, Components and How it works
In modern industrial and residential environments, electronic devices are becoming increasingly sensitive and vulnerable to electrical faults. Surge (also known as overvoltage transients) is one of the leading causes of system damage, resulting in major asset loss and operational disruption. The optimal solution to prevent this threat is a Surge Protection Device (SPD).
This article provides an in-depth overview of SPDs, helping you understand how they work, their classifications, and how to select the most suitable device for your system.
What is Surge?
Surge refers to the phenomenon in which lightning current, after striking the grounding system, transfers part of its energy through power lines or signal lines into the building, generating overvoltage transients that can damage electronic equipment.
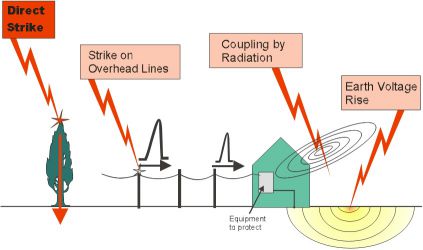
Causes of surge:
- Direct lightning strike to a structure: Lightning current concentrates at one point and propagates through electrical wiring.
- Lightning strike on conductive objects near the structure: Creates electromagnetic induction and generates voltage spikes.
- Electromagnetic induction caused by lightning: Lightning strikes nearby objects, creating strong magnetic fields that affect electrical conductors.
Damages caused by surge:
- Damage to electronic equipment: Computers, telecommunication devices, control systems…
- Fire or explosion: Due to heat generated from overvoltage currents.
- Operational interruptions: Affects business operations and daily activities.
What is a Surge Protection Device?
What is a Surge Protection Device? It is a device designed to protect electrical and electronic equipment from voltage spikes (overvoltage) caused by lightning strikes or switching operations on the power grid.
- English name: Surge Protection Device (SPD) or Transient Voltage Surge Suppressor (TVSS).
- Function: When detecting a surge that exceeds the permitted limit, the SPD immediately diverts the excess energy to the ground within a very short time (a few nanoseconds), thereby limiting the voltage reaching the equipment and preventing damage.
Key difference: Surge protection safeguards internal devices (electrical equipment, computers, servers) from voltage spikes, while lightning protection against direct strikes protects external structures (buildings, roofs) from direct lightning current.
Functions and importance of surge protection devices
The functions of surge protection devices are undeniable, especially in high-value systems:
- Equipment protection: Prevents permanent damage or reduced lifespan of sensitive devices (PLCs, computers, cameras, network equipment).
- Data protection: Ensures data continuity and integrity for server and network systems.
- Maintains operation: Minimizes downtime due to electrical incidents, especially important for production lines and security systems.
Surge Protection System
What is a surge protection system? It is an integrated solution consisting of multiple protection stages installed at strategic points in the electrical system, following international standards (typically three protection levels: Type I, Type II, Type III). A complete surge protection system includes:
- Primary surge protection device (power surge protection).
- Secondary surge protection device (signal/network surge protection).
- Standard grounding (earthing) system.
Classification and Technical Structure
Classification by structure and application
- Classification by power type:
- AC Surge Protection Device: For alternating current, commonly used in residential and industrial power networks.
- DC Surge Protection Device: For direct current, often found in solar (PV) and telecommunication systems.
- Classification by application:
- Power line surge protection: Installed in main or sub-distribution panels to protect primary power sources.
- Signal line surge protection: Protects data transmission lines such as network cables (RJ45 network), camera lines, and control signals.
Classification by phase and protection level
- Classification by phase:
- Single-phase surge protection: Common in residential systems or standalone loads (e.g., 120/240VAC single-phase surge protector).
- Three-phase surge protection: Used in large industrial systems, available in 3P or 3P+N 40kA, 3P+N 65kA versions.
- Classification by Type (IEC 61643 Standard):
- Type I: Installed at the service entrance, capable of handling high direct lightning currents.
- Type II: Installed at main distribution boards, protecting against residual surges.
- Type III: Installed near end devices (sockets, PDU), providing final-level protection.
Structure and working principle
The structure of surge protection devices mainly relies on nonlinear components such as:
- Varistor (MOV – Metal Oxide Varistor): The most common component. It acts as an open switch under normal voltage but switches to conduction when voltage spikes (SPD working principle), diverting surge current to the ground.
- TVS Diode (Transient Voltage Suppression Diode): Used primarily for sensitive signal lines.
- Spark Gap/Gas Discharge Tube (GDT): Used for high-level protection (Type I).
Important technical specifications
Understanding SPD technical specifications is essential when selecting a device:
- Uc (Maximum continuous operating voltage): The highest voltage that the SPD can withstand continuously without triggering.
- Up (Voltage protection level): The maximum voltage your equipment experiences when the surge is suppressed. The lower, the better.
- In (Nominal discharge current): Surge current the SPD can handle once while maintaining performance.
- Imax (Maximum discharge current): The maximum surge current the SPD can withstand before needing replacement.
Installation Guide and Practical Applications
How to choose the right device
Selecting an SPD requires evaluating the installation environment:
- For homes/small offices: Prioritize Type II and Type III SPDs, single-phase types for power lines, and network surge protectors (RJ45).
- For factories/large facilities: Use all three levels: Type I, Type II, and Type III, with three-phase models featuring high Imax/In ratings.
Wiring diagram and installation
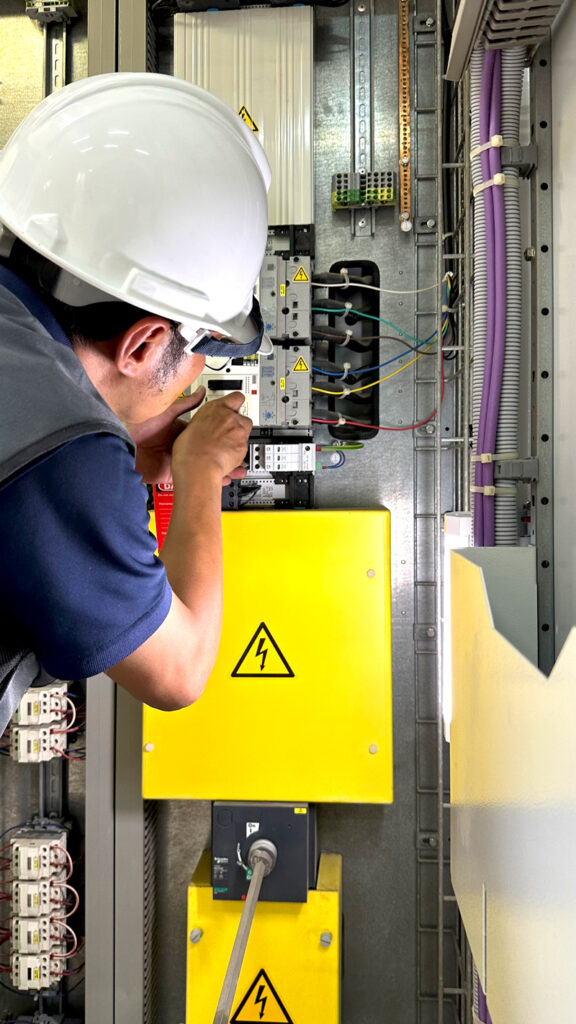
Installation must strictly follow standards. A surge protection wiring diagram typically shows parallel installation to the power line (Line and Neutral) and connection to the grounding system.
- Basic SPD wiring: Use the shortest possible conductor from the SPD to the grounding bar to reduce wire inductance and ensure fast surge discharge.
Applications
SPDs are not only for power lines but also for many other systems:
- Surge protection for power systems: Protects all loads from the main distribution board using high-capacity SPDs.
- Surge protection for network systems: Protects switches, routers, and PCs. Example: APC PNET1GB surge protector.
- Surge protection for cameras: Protects both power supply lines and signal transmission (video/data).
Inspection and maintenance
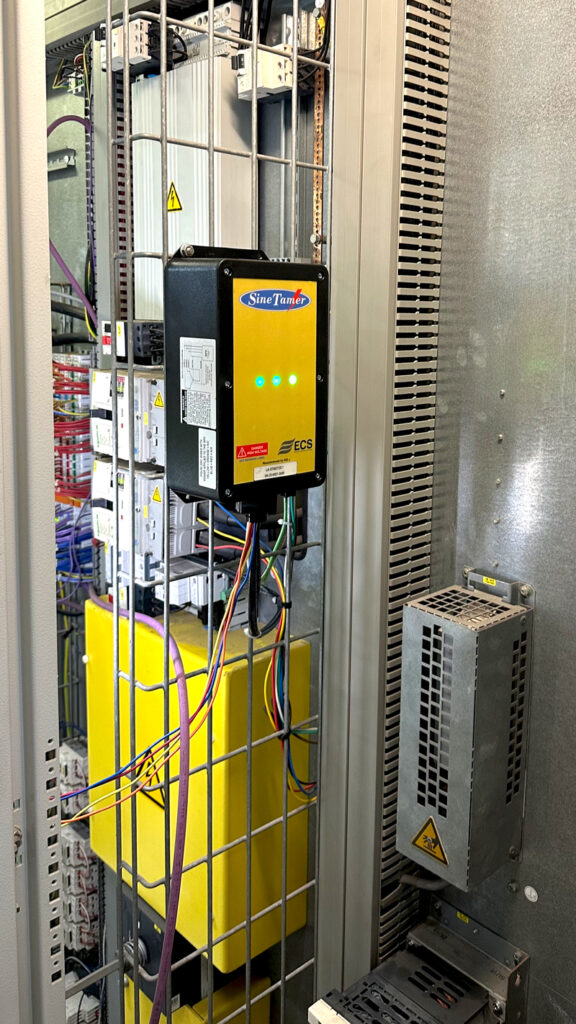
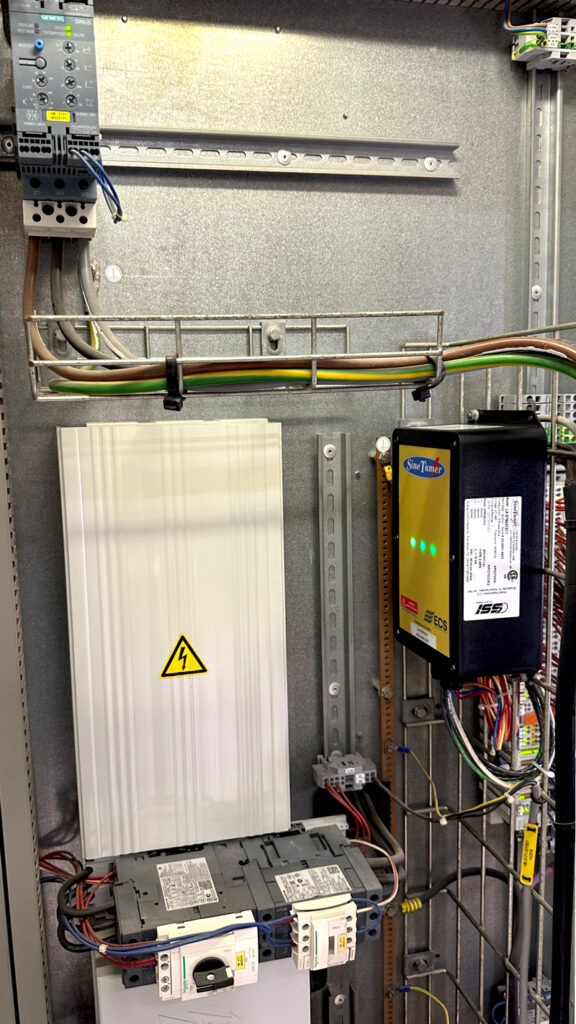
The simplest SPD inspection method is checking the status indicator light. Most modern SPDs have green indicators (working) and red/off (needs replacement). Regular SPD inspection every 6 months is recommended.
Popular Surge Protection Brands and Buying Advice
Top surge protection brands
To ensure effective protection, choosing reputable brands is crucial. Below are popular brands offering advanced and standard protection solutions:
- SineTamer (USA): Well-known for its Frequency Attenuation Network (FAN) technology, providing fast and effective surge suppression, widely used for critical applications.
- Schneider Electric (France): Renowned Acti9 product line, offering diversified solutions for electrical and industrial systems, including Schneider single-phase and three-phase SPDs.
- ABB (Switzerland – Sweden): Supplies high-quality SPDs often integrated into complete electrical solutions.
- Citel (France): Specializes in surge protection technology, including Citel surge protectors for power and signal lines.
- OBO Bettermann (Germany): Focuses on comprehensive lightning and surge protection solutions.
- APC (USA): Popular for IT and home protection devices, such as APC surge protectors.
Recommendations for selecting and installing SPDs
- Prioritize low Up: Choose devices with the lowest possible voltage protection level for maximum protection.
- Certification required: Ensure products are certified (IEC, UL, CE).
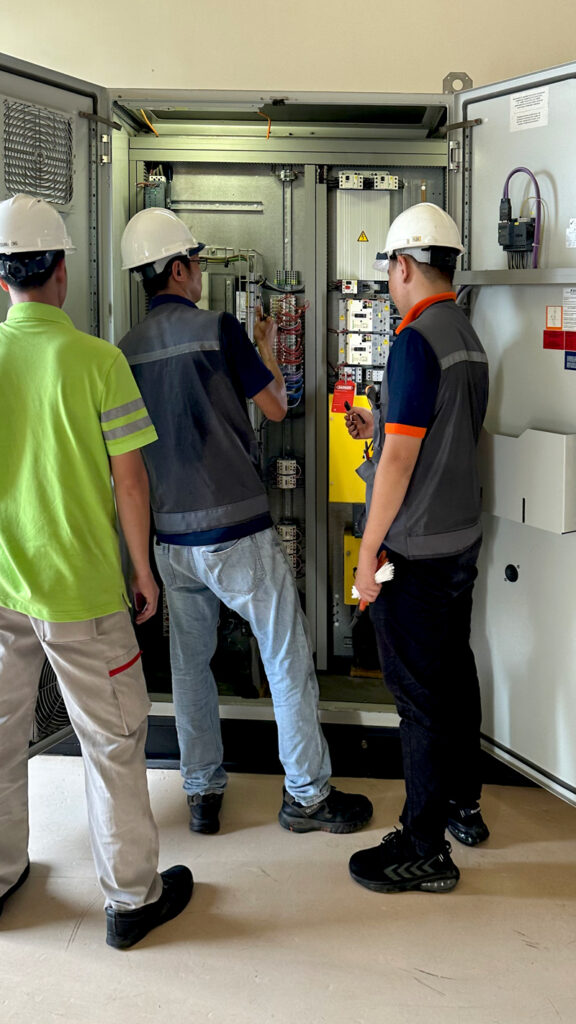
- Professional installation: Installation should be carried out by experienced technicians to ensure short conductor lengths and proper grounding.
Servo Dynamics Engineering: Authorized distributor of SineTamer in Vietnam.
Do not let surge transients become a constant threat to your assets and operations. Investing in a surge protection device is a smart choice to ensure stability and long-term system durability.
For professional consulting on high-standard surge protection solutions and installation services:
Servo Dynamics is the official distributor of SineTamer in Vietnam
For more detailed advice on selecting and installing surge protection systems, please contact Servo Dynamics.

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt