Consulting, Industrial Automation, News, Solutions
What is Industrial Electrical Cable? A Guide to Choosing the Right Cable
Industrial electrical cables play a crucial role in energy transmission and ensuring the stable operation of electrical systems in industrial environments. With the ability to withstand harsh conditions and meet high technical demands, industrial cables not only protect equipment but also enhance work efficiency. This article provides an overview of industrial electrical cables, covering popular types, structure, operating principles, and guidance on proper selection and installation.
What is an Industrial Electrical Cable?

Industrial electrical cables are specialized conductors designed to transmit high electrical currents in harsh industrial environments. They are constructed to withstand high temperatures, significant pressure, and various physical and chemical impacts. Industrial electrical cables play an essential role in supplying power to factories, plants, construction projects, and other production activities.
Types of Industrial Electrical Cables

1. Classification by Conductor Structure
- Flexible Cables: The conductor is made up of multiple fine strands twisted together, offering high flexibility, suitable for frequently moving positions.
2. Classification by Structure
- 2-core Cable: Used for simple electrical circuits and 2-phase equipment.
- 3-core Cable: The most common type, used for 3-phase circuits and industrial electrical devices.
- 4-core Cable: Designed for control systems, signal transmission, or specialized circuits.
3. Classification by Outer Sheath
- Round Cable: The most common shape, easy to manufacture and install.
- Oval Cable: A unique shape that saves space when installed in cable trays.
- Suping Cable: The outer sheath is reinforced with fiberglass, increasing mechanical durability.
4. Classification by Core Material
- Copper Core Cable: Offers high electrical conductivity, stable current transmission, and is commonly used in high-reliability systems.
- Aluminum Core Cable: Lighter and more cost-effective than copper but with lower conductivity. Suitable for systems that do not require high conductivity.
5. Classification by Voltage
- Low Voltage Cable: For electrical systems with voltage below 1kV.
- Medium Voltage Cable: For systems with voltage ranging from 1kV to 35kV.
- High Voltage Cable: For systems with voltage above 35kV.
6. Classification by Application:
- Control Cable: Used to transmit control signals to devices.
- Power Cable: Used to transmit electrical energy to motors, pumps, etc.
- Fire-Resistant Cable: Suitable for environments with high fire risk.
- Oil-Resistant Cable: Designed for environments with oil exposure.
- Heat-Resistant Cable: For use in high-temperature environments.
Structure of Industrial Electrical Cables
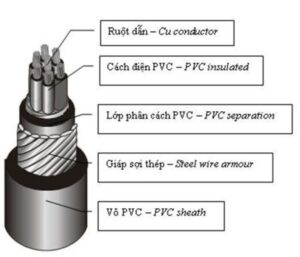
Industrial electrical cables are an indispensable component of industrial electrical systems. They are specially designed to ensure stable, safe, and efficient power transmission even under harsh working conditions.
The general structure of an industrial electrical cable consists of the following parts:
- Conductor
- Material: Typically made of copper or aluminum. Copper offers better conductivity but is more expensive, while aluminum is lighter and more affordable.
- Shape: Can be either solid or stranded. Stranded conductors increase flexibility and resistance to bending.
- Insulation
- Function: Separates the conductor from other cable components and the external environment, ensuring electrical safety.
- Material: Commonly made of PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), XLPE (Cross-linked Polyethylene), or EPR (Ethylene Propylene Rubber). Each material offers unique advantages and disadvantages in terms of heat resistance, chemical resistance, and mechanical durability.
- Shielding
- Function: Protects the conductor from electromagnetic interference, enhancing signal stability.
- Material: Usually made of aluminum foil or copper mesh.
- Jacket
- Function: Protects the internal layers from mechanical, chemical, and environmental impacts.
- Material: Commonly made of PVC, rubber, or other synthetic materials.
- Other Components
- Filler: Helps enhance roundness, rigidity, and reduces cable deformation.
- Reinforcement fibers: Increases the mechanical strength of the cable.
Operating Principles of Industrial Power Cables
Industrial power cables operate based on the fundamental principles of electricity: transmission of electric current. When a voltage is applied across both ends of a conductor (cable core), an electric field is created within the conductor. Under the influence of this electric field, free electrons within the conductor move directionally from the negative pole to the positive pole. This directional movement of electrons constitutes an electric current.
The structure of industrial power cables supports this current transmission process:
- Conducting core: The pathway for the electric current to flow. The core material (copper or aluminum) has low resistivity, minimizing energy loss during transmission.
- Insulation layer: Prevents current leakage, protecting users and other equipment. It also helps avoid short circuits.
- Protective layer: Shields the insulation layer and conducting core from mechanical, chemical, and environmental damage.
Electric Power Transmission Process:
- Power source: Generates voltage and supplies energy to the electrical circuit.
- Power cable: Transmits electric current from the power source to the load (consuming device).
- Load: Consumes electrical energy and converts it into other forms of energy (light, heat, mechanical energy, etc.).
Features and Benefits of Industrial Power Cables
Industrial power cables play a crucial role in industrial electrical systems. Selecting and using the right type of cable provides practical benefits. Below are some key advantages of industrial power cables:
Safety Assurance:
- Prevents short circuits: High-quality insulation prevents short circuits, protecting devices and users.
- Fire resistance: Some cables are fire-resistant, minimizing damage in case of incidents.
- Environmental protection: Prevents electrical leakage, reducing environmental hazards.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency:
- Stable power transmission: High-quality cables ensure stable energy transmission, reducing energy loss.
- Extends device lifespan: Provides stable power, prolonging the lifespan of electrical devices.
- Boosts productivity: Ensures continuous operation of production equipment, increasing productivity.
Cost Savings:
- Lower maintenance costs: High-quality cables require less maintenance and repair, reducing operational costs.
- Energy savings: Reduces energy loss during transmission, saving electricity costs.
Meets Technical Requirements:
- Withstands harsh conditions: Designed to operate in extreme environments, such as high temperatures, humidity, and exposure to chemicals.
- Diverse product range: Available in various types with specific features tailored to different applications.
- Compliance with standards: Manufactured according to international and Vietnamese technical standards, ensuring quality and safety.
Flexibility:
- Easy installation: Can be installed in various ways to meet space and structural requirements.
- Easy maintenance: Relatively simple to inspect, repair, and replace power cables.
Applications of Industrial Electrical Cables
Industrial electrical cables play a critical role in transmitting electrical power for production and business activities. They are widely applied in various fields, including:
Industrial electrical cables are extensively used across multiple sectors, such as:
- Heavy industry: Supplying electricity for large machinery, equipment, and control systems, ensuring device protection.
- Construction projects: Providing power for construction equipment and electrical systems in buildings.
- Manufacturing plants: Powering production lines, motors, and automation systems.
- Energy sector: Transmitting power and connecting solar and wind energy systems.
- Oil and gas industry: Delivering electricity to extraction and processing equipment.
- Transportation: Supplying power to vehicles and traffic signal systems.
- Electronics and telecommunications: Powering telecommunications systems and data centers.
Technical Standards
To ensure quality and safety, industrial electrical cables must adhere to strict technical standards. Some common standards include:
National Standards: TCVN (Vietnamese Standards)
- TCVN 5935: Regulations for power cables.
- TCVN 9208: Guidelines for the installation of cables and electrical conductors in industrial projects.
International Standards: IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission)
- IEC 60502: Power cables with thermoplastic insulation.
- IEC 60228: Conductors made of copper or aluminum with thermoplastic insulation.
Important Considerations When Selecting Industrial Electrical Cables
When choosing industrial electrical cables, you need to consider the following factors to ensure efficiency and safety for the system:
- Rated voltage and current: Must match the requirements of the equipment and load.
- Conductor material: Copper or aluminum, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Insulation material: PVC, XLPE, EPR, etc., each offering different heat resistance and chemical durability.
- Operating conditions: Temperature, humidity, surrounding environment (oil, chemicals, etc.).
- Installation method: Underground, overhead, inside conduits, etc.
- Quality standards: TCVN, IEC, ANSI, etc.
- Brand: Choose reputable brands with quality certifications.
- Cost: Balance between quality and price.
Industrial Electrical Cable Installation Process
The industrial electrical cable installation process typically includes the following steps:
- Preparation
- Design inspection: Ensure the electrical system design complies with standards and project requirements.
- Material preparation: Ensure all necessary cables, conduits, accessories, and tools are available.
- Cable quality check: Inspect technical specifications, sheath condition, and cable cores.
- Installation
- Trenching: Dig trenches (for underground installations) as per design, ensuring appropriate depth and width.
- Conduit installation: Install protective conduits, ensuring alignment, slope, and absence of obstructions.
- Cable pulling: Pull cables through conduits or cable trays, taking care not to damage or break them.
- Cable splicing: Use suitable connectors to splice cables, ensuring secure and waterproof joints.
- Junction box installation: Install junction boxes at necessary points for branching or protecting cable joints.
- Device installation: Install electrical devices such as circuit breakers, switches, sockets in junction boxes.
- Route inspection: Recheck the entire cable route to ensure no errors.
- Testing
- Insulation resistance testing: Check the cable’s insulation resistance.
- Circuit testing: Ensure the electrical circuit operates stably.
- Grounding system testing: Verify the grounding system.
- Handover
- Documentation completion: Finalize the acceptance documents.
- Handover to the investor: Transfer the completed electrical system to the investor.
Industrial Electrical Cable Maintenance

Maintaining industrial electrical cables is essential to ensure stable, safe operations and prolong the cable’s lifespan. This helps prevent issues such as electrical shorts, circuit malfunctions, and reduces the risk of fire, ensuring uninterrupted production and business operations. Some key maintenance activities include:
Regular Inspections:
- Appearance: Inspect for cracks, wear, or deformation of the cable’s outer sheath.
- Connections: Check if connections are secure and free from oxidation.
- Cable Positioning: Verify that cables are not under heavy objects or show signs of rodent damage.
Insulation Resistance Measurement: Test the insulation between the cable core and sheath, as well as between individual cores.
Temperature Testing: Monitor cable operating temperatures to ensure they are within allowable limits.
Cleaning: Clean cable installations, removing dust, dirt, and grease.
Repairs: Fix any detected damages, such as replacing faulty sections or welding connections.
Top Industrial Electrical Cable Brands
Belden
Advantages: Belden, a renowned American brand, specializes in high-quality industrial cables widely used in industries demanding high reliability.
Applications: Commonly used in automation, oil and gas, and energy sectors.
Cadivi
Advantages: As one of Vietnam’s leading cable manufacturers, Cadivi is known for its consistent quality, reasonable prices, and diverse product range.
Applications: Extensively used in construction, factories, and enterprises.
DAPHACO
Advantages: DAPHACO offers high-quality cables that meet international standards. Their products are praised for durability and heat resistance.
Applications: Suitable for industrial, residential, and infrastructure projects.
CADI-SUN
Advantages: CADI-SUN is another reputable Vietnamese brand offering diverse, high-quality, and competitively priced products.
Applications: Used in construction, factories, enterprises, and large-scale projects.
Nexans
Advantages: Nexans is one of the world’s largest cable manufacturers, providing solutions for various industries. Their cables are designed for performance, reliability, and safety.
Applications: Utilized in energy, construction, automotive, and other industrial sectors.
Servo Dynamics – Authorized Distributor of Belden in VietNam
Servo Dynamics is the official distributor of Belden in Vietnam, offering a wide range of Belden cables and connectivity solutions. With extensive experience and a strong market reputation, Servo Dynamics has established itself as a reliable partner for many businesses in Vietnam.
Why Choose Servo Dynamics?
- Genuine Products: Committed to providing authentic Belden cables with guaranteed quality and high performance.
- Product Variety: Meeting diverse industrial needs with various cable types, such as Ethernet cables, optical fibers, coaxial cables, and control cables.
- Professional Technical Support: An experienced technical team offering guidance and support in selecting the right products.
- Excellent After-Sales Service: Providing fast and professional warranty and repair services.
Contact Servo Dynamics today for expert advice and tailored industrial cable solutions for your business!

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt