Consulting
What is EtherCAT? Working Principle & Industrial Applications
What is EtherCAT (Real-Time Communication Protocol)?

Definition of EtherCAT
EtherCAT (Ethernet for Control Automation Technology) is a high-performance, open-source Industrial Ethernet network system. It is a real-time Ethernet-based protocol optimized for automation applications. While it utilizes the physical infrastructure of standard Ethernet, it changes the data processing method to achieve ultra-high speeds and the lowest possible latency. Unlike traditional networks, EtherCAT processes data in real-time at the hardware level.
Who developed EtherCAT?
EtherCAT was first introduced by Beckhoff Automation in 2003. To popularize this technology, Beckhoff founded the EtherCAT Technology Group (ETG). Today, it is the world’s largest Industrial Ethernet organization with over 7,000 members (including giants like Omron, Mitsubishi, and Panasonic), ensuring neutrality and cross-manufacturer compatibility.
How is EtherCAT different from standard Ethernet?
- Standard Ethernet (TCP/IP): Data is sent in packets. Each device receives, decodes, processes, and then responds. For 100 nodes, the Master must send 100 separate packets, causing a “bottleneck” effect.
- EtherCAT: Uses an “on-the-fly” processing method. A single frame passes through all nodes. Each node extracts its data and inserts response data into the frame without stopping the data flow. This allows for maximum utilization of the 100Mbps Ethernet bandwidth.
Outstanding Advantages of EtherCAT
- Superior Speed: Can update 1,000 digital I/O signals in just 30 µs.
- Synchronous Precision: Time deviation between axes is measured in nanoseconds.
- Hardware Savings: No switches or routers are required in the local network, significantly reducing installation costs.
Structure & Components in an EtherCAT System
A standard EtherCAT system includes the following basic components:
What is an EtherCAT Master?
The Master is the management unit for the entire network. A unique feature of EtherCAT is that the Master can be deployed on any PC with a standard Ethernet port (NIC). No expensive specialized cards are needed; the Master uses control software like TwinCAT (Beckhoff), Codesys, or open-source libraries like SOEM or LinuxCNC for control.
What is an EtherCAT Slave?
Slaves are end devices such as Servo Drives, inverters, sensors, or I/O modules. Unlike the Master, Slaves must be equipped with a specialized processing chip called an ESC (EtherCAT Slave Controller). This chip handles data processing at hardware speed, bypassing software delays.
Common Slave Device Categories:
- EtherCAT Drive & Servo: Motion controllers supporting the CoE (CiA402) profile.
- I/O Modules: Data acquisition units for digital/analog signals from sensors.
- EtherCAT Coupler: Gateway devices between the main network and expansion modules (e.g., Beckhoff’s EK1100 series).
- Junction/Terminal: Used for Star topology or extending connection distances.
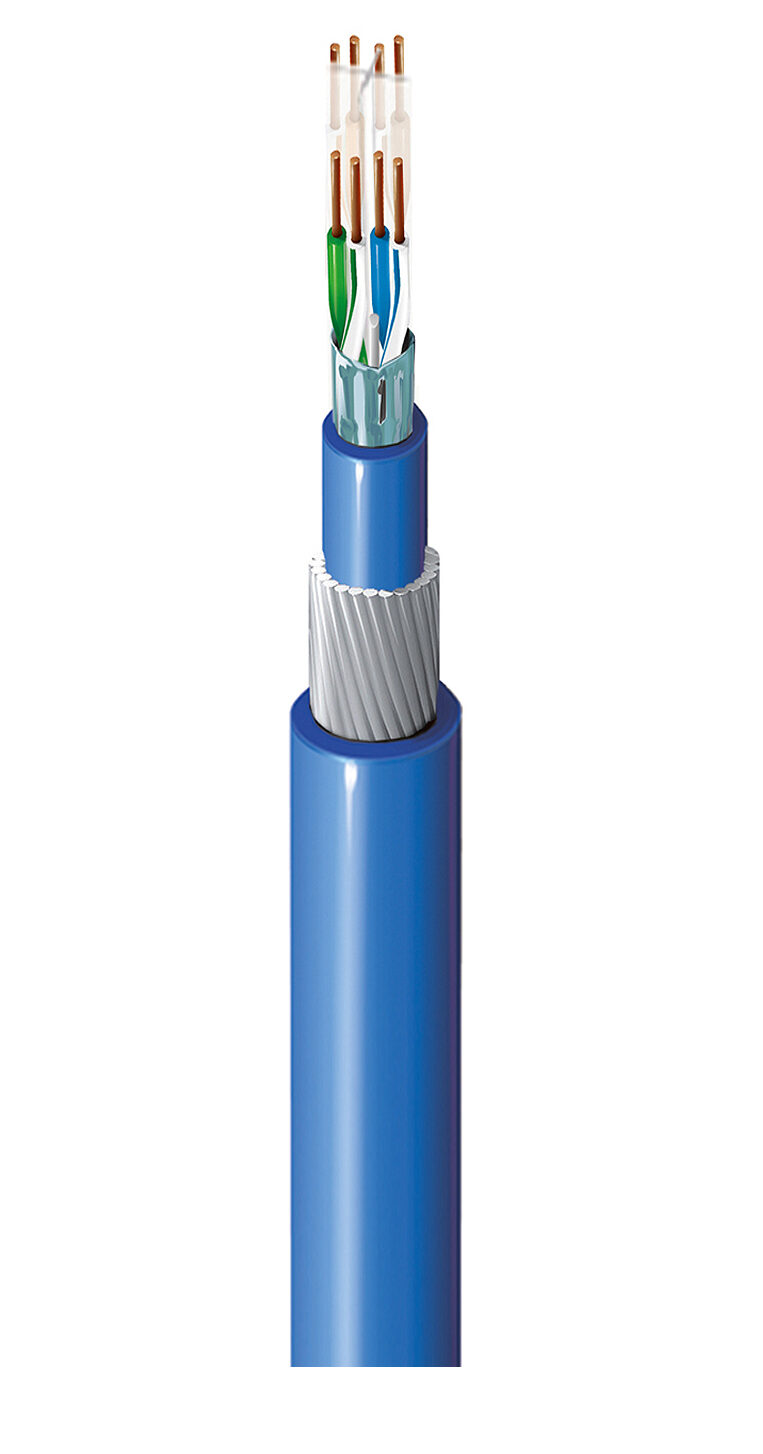
Transmission Cable (EtherCAT Cable)
Standard Ethernet cables (usually Cat5e or Cat6) are used. However, in industrial environments, STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) cables are preferred for electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection, along with industrial-grade M12 or RJ45 connectors to withstand vibration.
In-depth Working Principle of EtherCAT
“On-the-fly” Processing Mechanism
Imagine a train (Ethernet frame) running through stations (Slaves). At each station, workers don’t stop the train; instead, they hop on to grab their cargo and throw new cargo into the carriage while the train is moving. Once the train completes the loop and returns to the central station (Master), all data is updated.
Distributed Clock (DC) – The Key to Synchronization
To control 100 robot arms to lift an object simultaneously, they must share a common timeframe. EtherCAT uses the Distributed Clock mechanism:
- The Master sends a signal to measure transmission delay between nodes.
- Each Slave has an internal clock adjusted for that delay.
- Result: All devices in the network are synchronized within < 100ns.
PDO & SDO Data Transmission
- PDO (Process Data Object): Cyclic data used for critical high-speed info (e.g., actual position, velocity).
- SDO (Service Data Object): Acyclic data used for parameter settings, error reading, or initial configuration (usually via CoE).
EtherCAT State Machine (ESM)
Every Slave device must follow a strict state transition process for safety:
- Init: Initialization, no communication.
- Pre-Operational: Configuration setup (SDO).
- Safe-Operational: Reads data from Slave but hasn’t sent control commands yet.
- Operational: Full operational state, allowing motion control.
Key Industrial Applications of EtherCAT
- Motion Control: The most common application. Synchronous multi-axis control in high-speed packaging and labeling machines.
- CNC Machine Tools: Ensures smooth cutting paths thanks to ultra-fast position interpolation.
- Robotics & Cobots: The top choice for 6-axis and collaborative robots due to precise force and position feedback.
- AGV/AMR Autonomous Vehicles: Connects drive wheels, LiDAR sensors, and battery management systems.
- Semiconductor Production: Requires cleanroom environments and micrometer-level precision.
5. Comparison: EtherCAT vs. Competitors
| Criteria | EtherCAT | Profinet (RT/IRT) | Ethernet/IP | Modbus TCP |
| Effective Bandwidth | > 90% | ~ 50% | ~ 10-20% | Low |
| Network Topology | Flexible (Line, Star, Tree, Ring) | Mostly Star/Line | Mostly Star | Star |
| Switch Requirement | Not required | Mandatory for IRT | Mandatory | Mandatory |
| Synchronization | < 1 µs | ~ 1 µs | Undefined | None |
Top Trusted EtherCAT Brands
Belden (Lumberg Automation & Hirschmann)
Belden is a global leader in industrial network infrastructure. Within the EtherCAT ecosystem, Belden focuses on the physical layer – the decisive factor for system stability:
- Specialized Cable Solutions: Belden offers DataTuff® Cat5e/Cat6 cables with oil-resistant jackets, UV resistance, and extreme temperature tolerance. Specifically, High-Flex cables for Cable Carrier applications in robotics.
- Lumberg Automation Connectors: M12 and RJ45 connectors designed for zero vibration, reaching IP67/IP68/IP69K ratings to ensure no Lost Frames in factory environments.
- EMI Protection: Belden cables feature advanced shielding technology, protecting EtherCAT data frames from high-frequency noise from high-power inverters and Servo motors.
Beckhoff Automation
The “father” of EtherCAT technology, Beckhoff provides the world’s most comprehensive ecosystem:
- PC-based Control: Turns powerful industrial PCs into true EtherCAT Masters.
- I/O Terminals: Thousands of I/O modules ranging from basic digital signals to high-speed measurement modules.
- TwinCAT Software: The standard global tool for EtherCAT programming and configuration.
Omron
Omron has deeply integrated EtherCAT into its Sysmac automation platform:
- Synchronization: NX/NJ Controllers coordinate perfectly with 1S Servo Drivers via EtherCAT for complex motion control tasks.
- Openness: Omron supports flexible connection with third-party devices via ESI file standards.
Mitsubishi Electric
Despite having its own protocol (CC-Link IE), Mitsubishi offers robust EtherCAT-supported Motion CPUs and Drivers for the Asian market, helping customers integrate their equipment into multinational systems.
Implementation & Troubleshooting Guide
Basic Setup Steps
- Master Configuration: Install the EtherCAT driver for the PC’s LAN port.
- Device Scanning: Use software (like TwinCAT) to auto-detect Slaves based on ESI (.xml) files.
- DC Configuration: Activate Distributed Clock if the system requires motion synchronization.
- PLC Programming: Map I/O variables to PDO memory areas.
Common Troubleshooting
- AL Status Code: Every error has a code (e.g., 0x0011 is an invalid configuration).
- CRC Error: Usually due to poor cable quality or EMI. Check RJ45 crimps or use Belden shielded cables.
- Working Counter (WKC) Error: Master sends a packet but the Slave doesn’t respond correctly. Often caused by broken wires or Slave power loss.
Servo Dynamics Engineering: Authorized Distributor of Belden in Vietnam
In an EtherCAT system, no matter how modern the Master and Slaves are, poor-quality transmission cables can lead to costly downtime.
Servo Dynamics Engineering is the official authorized distributor of Belden in Vietnam. We not only provide specialized anti-interference, oil-resistant, and high-flex EtherCAT cables but also offer in-depth technical consultancy to optimize your automation system.
Contact us today for the best industrial solutions!

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt