Consulting, Fire & Safety, News
What is Access Control? Structure, Applications, and Types
In the era of Industry 4.0, ensuring security and effective access management has become a crucial factor for buildings, factories, hospitals, and many other facilities. Access Control Systems not only enhance security but also offer outstanding benefits such as efficient personnel management, cost savings, and a more professional image. Let’s explore the structure, applications, and significance of these systems in the article below.
What is an Access Control System?

An Access Control System is an electronic security system designed to manage and control user access to a specific area, building, or facility. This system allows access permissions for individuals, tracks entry and exit history, and prevents unauthorized access.
Types of Access Control Systems
Access Control Systems are categorized based on technology and authentication methods. Below are some common types:
Fingerprint Access Control System:
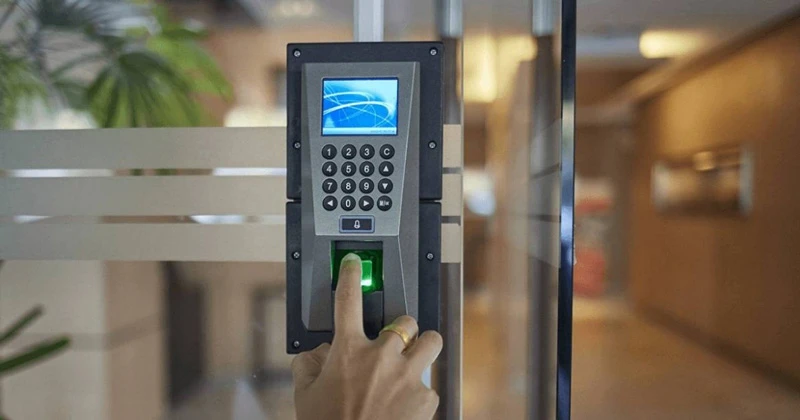

- Uses fingerprint scanners for authentication and door unlocking.
- Ensures high security as each fingerprint is unique.
- Often integrated with time attendance software to manage employees’ working hours.
Proximity Access Control System:
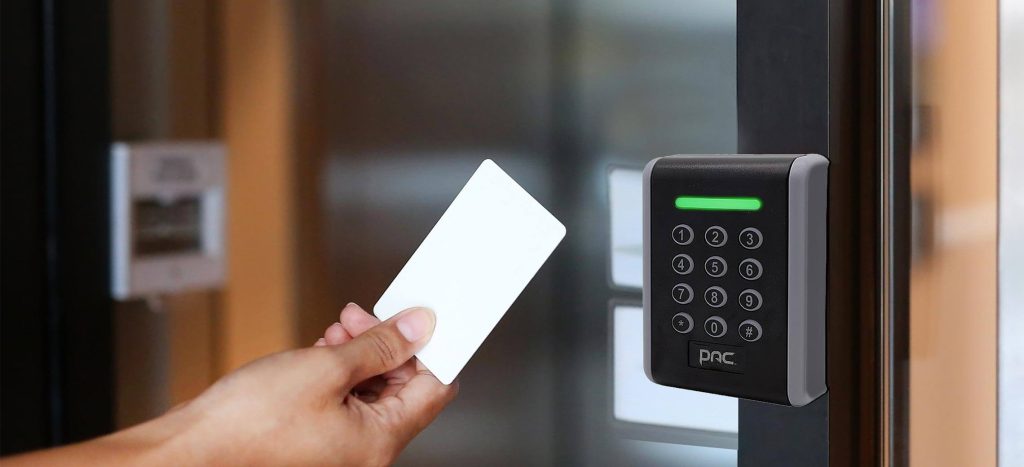

- Uses proximity cards for authentication.
- Cards can store personal information and grant access to specific areas.
- Data from proximity cards is stored and managed through specialized software.
Facial Recognition Access Control System:
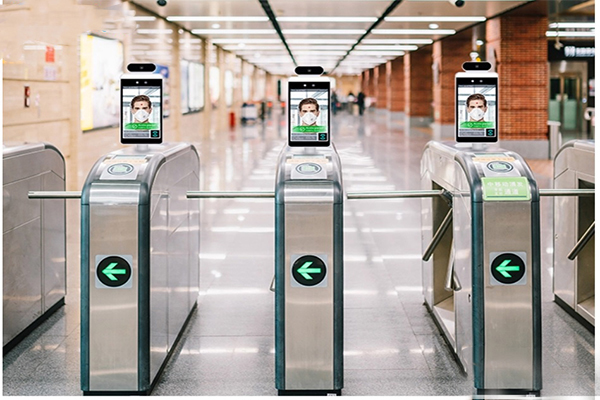

- Uses facial recognition technology for authentication.
- Provides high security and accuracy.
- Commonly used in environments requiring strict security measures.
PIN Code Access Control System:

- Uses PIN codes for authentication.
- Easy to implement and use but may be less secure if PIN codes are exposed.
Biometric Access Control System:
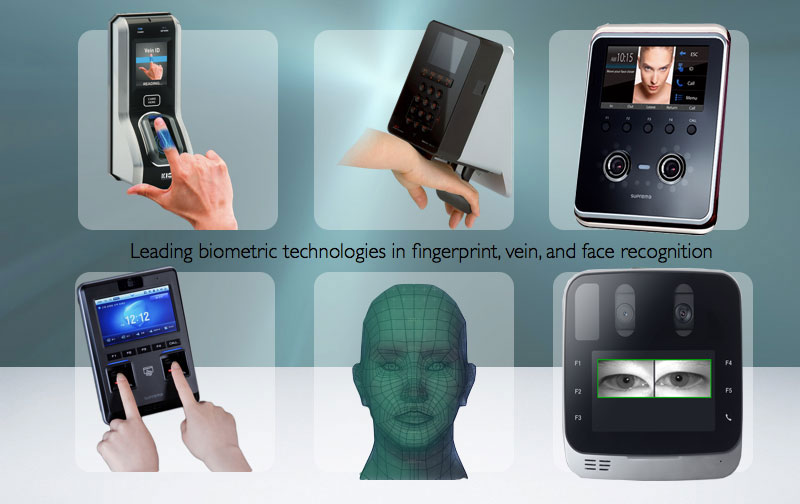

- Includes iris recognition, voice authentication, or other biometric methods.
- Offers high security and is difficult to forge.
These systems can be integrated to enhance security levels and cater to the specific needs of different organizations.
Structure of an Access Control System
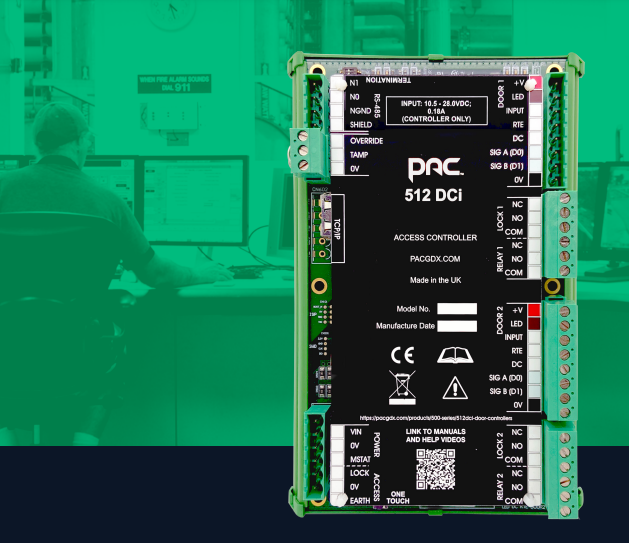

A basic Access Control System consists of the following components:
- Reader: A device that identifies access credentials (cards, fingerprints, facial recognition, or numeric codes).
- Controller: A device that processes information and controls door locking/unlocking.
- Electromagnetic Lock: A device that secures the door.
- Cards, fingerprints, facial recognition, numeric codes: User authentication methods.
Additionally, an Access Control System may include the following components:
- Management Software: Manages data and access permissions.
- Exit Button: Allows door unlocking from the inside.
- Door Sensor: Detects the door’s status.
Operating Principle of Access Control
The Access Control System operates in a closed-loop process, ensuring strict control over each entry and exit.
- Identity Verification: Users authenticate themselves by swiping a card, scanning a fingerprint, using facial recognition, or entering a PIN code.
- Data Transmission: The reader (Reader) sends the collected authentication data to the central controller (Controller).
- Processing & Authorization: The controller verifies the data and checks it against the list of authorized users.
- Access Grant or Denial: If the information is valid, the controller activates the electromagnetic lock to open the door; if not, the system denies access or triggers an alert.
- Logging & Monitoring: All access activities are recorded in the system for security management and monitoring purposes.
Features and Benefits of Access Control
Access Control Features
- Entry & Exit Control: Allows setting access permissions based on time, location, or user groups.
- Access History Logging: The system can store and generate detailed reports on entry and exit times, enabling close monitoring of employees and visitors.
- Alarms & Alerts: If unauthorized access or an invalid entry attempt occurs, the system triggers an alarm to prevent security breaches.
- System Integration: Can connect with other security devices such as cameras, fire alarm systems, and building management software to enhance security.
- Remote Management: Some modern systems support remote access through software or mobile applications, allowing monitoring and control from anywhere.
Benefits of Access Control
- Enhanced Security: Minimizes the risk of unauthorized access, protecting assets and personnel.
- Efficient Personnel Management: Easily track employee working hours and control individual access.
- Cost Savings: Reduces the need for security personnel, minimizes asset loss, and optimizes operational expenses.
- Professional Image: Utilizing advanced technology enhances the modern and professional image of businesses and organizations.
- High Durability and Flexibility: The system can be expanded and integrated with other technologies to meet future management needs.
- Reduced Risk of Loss: Using personal identification methods instead of physical keys significantly decreases the risk of theft or duplication.
How to Install an Access Control System
- Survey and Design:
- Determine the installation locations for readers, controllers, electromagnetic locks, and other devices.
- Select suitable readers, electromagnetic locks, and authentication methods based on project requirements.
- Design connection diagrams and equipment layout.
- Prepare Materials and Tools:
- Readers (card, fingerprint, facial recognition, PIN).
- Controller unit.
- Electromagnetic locks (magnetic lock, bolt lock, latch lock).
- Cards, fingerprints, or other authentication methods.
- Cables, conduits, and other electrical materials.
- Installation tools (pliers, screwdriver, drill, welding machine, etc.).
- Install Equipment:
- Readers: Install at convenient locations for users, usually near entry doors.
- Controller Unit: Install in an electrical cabinet or technical room.
- Electromagnetic Locks: Install securely on doors to ensure proper locking and safety.
- Other Devices: Install exit buttons and door sensors (if applicable) according to the design diagram.
- System Connection:
- Connect readers, controllers, electromagnetic locks, and other devices according to the design diagram.
- Use cables and conduits to ensure neat and safe connections.
- Thoroughly inspect all connections to prevent errors.
- Software Configuration:
- If the system includes management software, install it on a computer.
- Set up system parameters and assign user access permissions.
- Testing and Trial Run:
- Test system operation after installation.
- Ensure all devices function correctly.
- Fix any detected issues.
Note:
- It is recommended to hire professional technicians for Access Control system installation.
- Carefully read the manufacturer’s installation guide before proceeding.
- Ensure electrical safety during installation.
- Regularly inspect and maintain the system to ensure stable operation.
Applications of Access Control

- Office Buildings: Ensures security and manages employee and visitor access.
- Factories and Industrial Facilities: Controls entry to production areas, preventing unauthorized access.
- Hospitals and Schools: Manages entry for patients, students, and staff, enhancing safety.
- Hotels and Shopping Centers: Regulates guest access and integrates with payment and security camera systems.
- Residential Areas: Ensures safety for residents.
How to Choose an Access Control System
- Suitable Identification Technology:
- Select the appropriate identification technology (card, fingerprint, facial recognition, PIN code, etc.) based on project requirements.
- Consider security level, convenience, and cost of each technology.
- System Scale:
- Determine the number of users and doors that need to be controlled.
- Choose a system that can scale to meet future needs.
- Necessary Features:
- Identify essential system features (access control permissions, entry/exit logs, alarms, integration capabilities, etc.).
- Select a system that offers all the required functionalities.
- Investment Budget:
- Determine the budget for the access control system.
- Choose a system that fits within the budget constraints.
- Integration Capability:
- Assess the system’s ability to integrate with other systems (CCTV, fire alarm, building management, etc.).
- Select a system with flexible integration options.
- Support Services:
- Choose a provider that offers excellent support services, including consultation, installation, warranty, and maintenance.
Common Access Control Issues and How to fix:
1. Card Reader Issues:
Description: The card reader does not recognize the card, reads slowly, or reports an error.
Causes: Dust, physical damage, firmware errors, or poor connection.
Solutions:
- Clean the reader with specialized tools.
- Check and replace if there is physical damage.
- Update the firmware for the reader.
- Check the cable and power connections.
2. Software Glitches:
Description: The management software is not working, freezes, or displays incorrect information.
Causes: Software errors, software conflicts, insufficient system resources, or database errors.
Solutions:
- Restart the system.
- Update the software to the latest version.
- Check the system configuration and ensure sufficient resources.
- Restore the database from a backup (if available).
- Contact technical support if the problem persists.
3. Power Supply Problems:
Description: The system does not work, works intermittently, or experiences sudden power loss.
Causes: The power supply is damaged, loose connection, or overload.
Solutions:
- Check the power connections.
- Check and replace the damaged power supply.
- Check the backup power system (UPS) if available.
4. Connectivity Problems:
Description: The system cannot connect to the network, or the connection is interrupted.
Causes: Network cable errors, switch errors, router errors, or network configuration issues.
Solutions:
- Check the network cables and connections.
- Check the switch and router.
- Check the IP and DNS configuration.
- Contact the IT department for support.
5. User Credential Issues:
Description: Users cannot access, cards are rejected, or user information is incorrect.
Causes: Expired cards, lost cards, incorrect user information, or changed access rights.
Solutions:
- Check the card status (expired, canceled).
- Issue a new card if necessary.
- Update user information in the system.
- Check and adjust access rights.
- Instruct users on how to manage their cards and login information.
In addition, regular maintenance of the access control system is very important to detect and prevent potential problems. Keeping an event log is also helpful for diagnosing and troubleshooting issues.
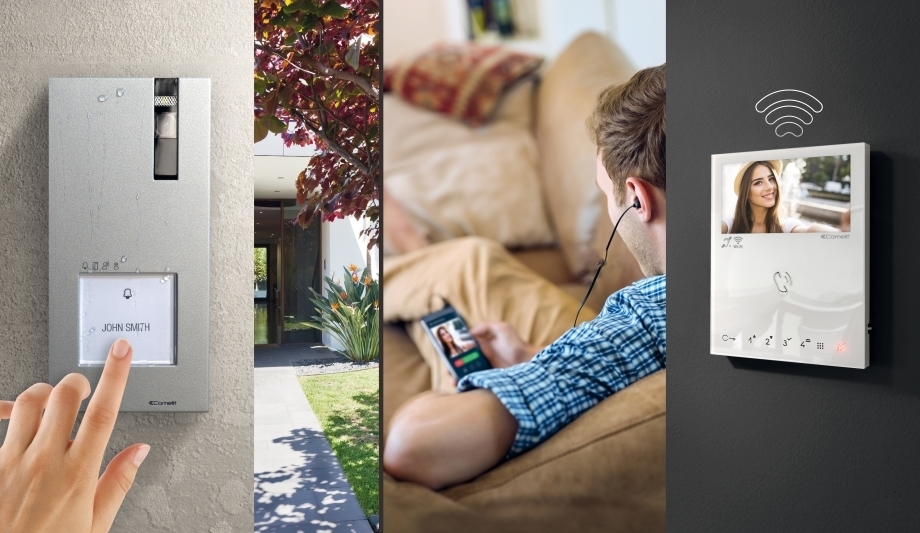
Comelit Access Control System
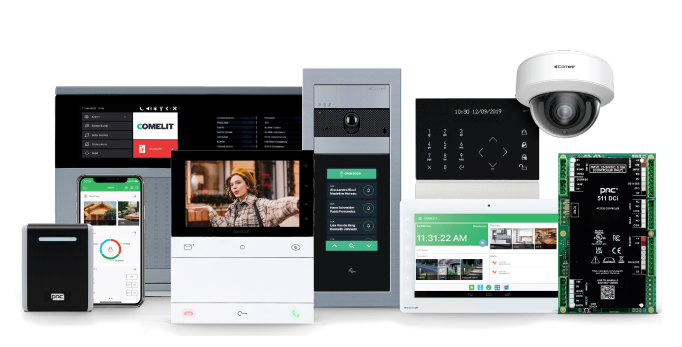
Comelit offers a modern access control solution designed to manage and monitor entry permissions for specific areas using advanced identification technologies such as facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, RFID cards, and PIN codes. The system seamlessly integrates with other security solutions, including surveillance cameras, fire alarm systems, and building management software, enhancing overall safety and operational efficiency.
Why Choose Comelit Access Control?
- Our solutions offer an end-to-end ecosystem of product from a variety of credentials, readers, controllers and management software.
- We enable solutions to be designed and installed to meet your customer needs.
- Our products support integration at a hardware and software level, for flexible expansion into a wide range of security, safety and building control systems.
- We offer lifetime product guarantees for our readers and ID devices.
- Our technical department offers engineer-to engineer support.
Servo Dynamics – Official Distributor of Comelit in Vietnam
Comelit is a globally recognized brand specializing in security and access management solutions. Its product range includes access control systems, intercom systems, surveillance cameras, and smart home solutions.
Servo Dynamics has extensive experience in distributing and installing security systems. Our team of highly trained and experienced technicians is ready to provide expert consultation, design, and installation services tailored to your specific needs.
Explore Comelit Products
Learn More

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt