News, Consulting, Solutions, Stratus Technologies
Edge Computing: What it is, Benefits, and How it Compares to Cloud
Edge Computing is transforming the way businesses process data by decentralizing computing and bringing processing closer to where data is created—at the “edge” of the network. Instead of relying solely on centralized cloud servers, edge computing technology enables real-time data analysis and decision-making, reducing latency and improving performance. This article will guide you through key concepts, real-world applications of edge computing, benefits of edge computing, and a detailed comparison between edge computing and cloud computing.
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to Edge Computing and the Data Explosion
Overview of Data Processing Trends in Modern Enterprises
In the era of Industry 4.0, the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Cyber-Physical Systems has created massive amounts of data (Big Data) at an unprecedented rate. Modern enterprises, especially those in industrial manufacturing and operations, not only need data but require the ability to process it instantly.
Why the Need for Edge Computing Emerged
Traditional Cloud Computing, despite its power, has one critical drawback: Latency. Sending terabytes of IoT sensor data to faraway data centers for processing and then returning control signals takes too long. For mission-critical applications like autonomous vehicles, real-time machine monitoring, or remote surgery, even milliseconds of delay can be disastrous.
The need for instant decision-making, reduced bandwidth consumption, and stable operations during poor connectivity is the core purpose of edge computing in Industry 4.0.
The Relationship Among IoT – Industry 4.0 – Edge Computing
- IoT (Internet of Things): The source of data—sensors, cameras, machines generating raw data.
- Edge Computing: The mechanism for processing data. It processes data at the source, converting raw data into actionable insights in real time.
- Industry 4.0: The application environment. Edge Computing enables smart factories, automation, predictive maintenance, and drives digital transformation in manufacturing.
What Is Edge Computing?

Definition of Edge Computing
What is Edge Computing? It is a distributed computing model in which data processing, analysis, and storage take place as close as possible to the physical location where the data is created (i.e., at the “edge” of the network).
Edge Computing enables the integration of existing control and automation applications into a unified platform, while supporting additional mission-critical applications. The goal is to improve operational performance by bringing computing resources closer to critical devices where operational data is generated.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
Edge Computing works by processing data at the location where it is generated instead of sending it to centralized data centers or cloud servers. Below is the typical operation of the edge computing model:
- Data creation at the edge: Devices such as IoT sensors, AI cameras, and industrial machines generate raw data (sensor readings, images, real-time metrics).
- Processing at Edge Nodes: Data is sent to nearby edge devices (Edge Gateways, Edge Servers). These devices filter, compress, analyze, and run AI/ML models in real time.
- Instant decision-making: Decisions are made immediately based on local analysis. Example: a CNC machine adjusts cutting speed when detecting abnormal vibrations.
- Sending essential data to the Cloud: Only summarized, filtered, or complex analytical results are sent to the cloud for long-term storage or large-scale analysis.
Components of an Edge Computing Architecture
Edge computing architecture consists of multiple collaborating layers:
- Edge Devices: The data-generating layer—sensors, cameras, machines, mobile devices.
- Edge Nodes: Higher-capacity devices (Edge Gateways, industrial mini-PCs, industrial control panels) performing primary data processing.
- Edge Gateway: Acts as the computing interface, managing data flow, security, and connections between IoT devices and local/cloud servers.
- Cloud Datacenter: Handles large-scale storage, AI model training, and centralized analytics.
What is Edge Computing in IoT?
Edge Computing in IoT refers to deploying analytics and AI applications directly on IoT devices or gateways. This enables independent decision-making—for example, an AI security camera identifying objects and sending only alerts (processed data) instead of entire video streams (raw data).
Applications of Edge Computing in Enterprises
Edge computing applications are spreading across all industries, especially where instant action and ultra-low-latency data processing are required:
Industrial Manufacturing & Smart Factories:
- Predictive Maintenance: Analyzing machine vibration and temperature at the edge to detect potential failures.
- Real-time Quality Control: Edge AI cameras detect defects instantly on production lines.
Autonomous Vehicles, Robots, IoT Sensors:
- Self-driving cars: Processing camera and LiDAR data within milliseconds for navigation and braking.
- AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles): Using edge computing devices for real-time mapping and warehouse navigation.
Security Monitoring – AI Edge Cameras:
- AI cameras identify faces, detect intrusions, or count people without transmitting full video streams, saving bandwidth and increasing security.
Smart Retail:
- Automated inventory management, in-store customer behavior analytics, and real-time POS processing.
Telecommunications (5G – MEC):
- Mobile Edge Computing (MEC): Deploying edge servers at 5G base stations, enabling ultra-low-latency applications like VR and online gaming.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Edge computing provides numerous strategic benefits, especially amid digital transformation:
Faster Processing (Reduced Latency)
This is the biggest advantage. Processing data close to its source significantly reduces latency, enabling real-time decision-making essential for automation and safety systems.
Improved Data Security
Sensitive data is processed and stored locally, reducing exposure during transmission and improving privacy compliance (e.g., HIPAA).
Lower Transmission & Bandwidth Costs
Only essential or aggregated data is sent to the cloud, reducing network load and operational costs.
Reliable Operation with Poor Internet Connectivity
Edge nodes can operate independently during network outages, ensuring system resilience (e.g., factories, ships, remote areas).
Optimized for Digital Transformation
How does Edge Computing support digital transformation? It enables automation, increases efficiency, and allows businesses to focus on high-value tasks.
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing
Edge and Cloud are not competitors—they complement each other in modern data architectures.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing provides computing resources (servers, storage, databases, networking, software) over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis.
- Main Cloud models:
- IaaS: Virtual machines and storage.
- PaaS: Application development environments.
- SaaS: Software delivered via the internet.
- Benefits: Unlimited scalability, reduced upfront costs, easy management.
Similarities Between Edge and Cloud
- Both are computing technologies for data processing.
- Both support IoT, AI, and digital transformation.
- Both use compute & storage resources.
Differences
| Feature | Cloud Computing | Edge Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Location | Centralized data centers. | At the network edge, near data sources. |
| Latency | High. | Very low (typically under 10 ms). |
| Security | Risks during data transmission. | Higher security due to local processing. |
| Scalability | Near-infinite scalability. | Limited by local edge device capacity. |
| Deployment Cost | Operational costs and bandwidth. | Higher initial hardware investment. |
| Main Purpose | Long-term storage, deep analytics, AI training. | Real-time processing and offline operation. |
When to Use Edge vs. Cloud?
- Edge is ideal for: Real-time processing, low latency apps, unstable networks, sensitive data.
- Cloud is ideal for: Long-term storage, large-scale analytics, AI training.
Hybrid Edge + Cloud: Edge handles real-time workloads, while Cloud handles long-term analytics and AI training.
Edge–Cloud Deployment Models in Industry 4.0
Hybrid Edge – IoT – Cloud
IoT sensors send data to Edge Gateways for local control and analysis, then synchronized with cloud systems for overall management.
Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) with 5G
Edge servers placed at 5G base stations enable high-performance applications like AR/VR, autonomous robots, and remote operations.
Real-world Examples in Manufacturing, Logistics, and Energy
- Manufacturing: Edge Servers inside industrial cabinets analyze compressor data and instantly shut down machines during anomalies.
- Logistics: Trucks with edge devices process route and cargo sensor data even without connectivity.
Typical Edge Computing Devices & Architectures
To deploy edge computing, industrial-grade hardware is required:
Edge Gateway and IoT Sensors
- IoT Sensors: Temperature, pressure, vibration sensors.
- Edge Gateway: Collects sensor data, performs light analytics, compresses data, and provides security.
Edge Servers
Industrial-grade computers capable of heavy workloads such as AI models, virtualization, and real-time analytics.
Edge Orchestration Software
Edge environments require remote management. Platforms like Azure IoT Edge and AWS IoT Greengrass help manage thousands of devices.
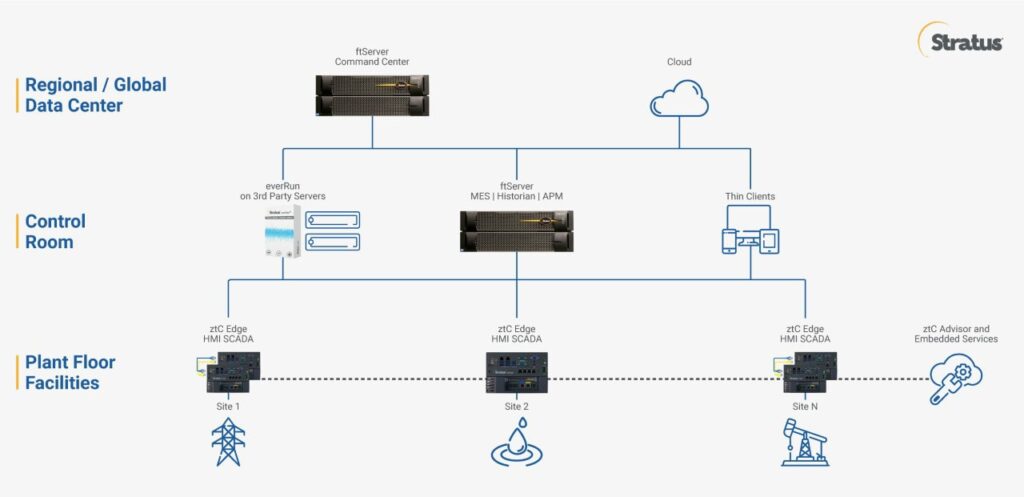
Reliable Edge Computing Example: Stratus Technologies
Platforms such as ftServer and ztC Edge are built for industrial environments requiring high availability:
- Simple & Automated: Easy deployment, built-in virtualization and fault tolerance.
- Protected & Durable: Industrial-grade design, wide temperature tolerance, robust reliability.
The Future of Edge Computing
The future of edge computing technology includes deeper integration with the Cloud:
Edge AI
AI/ML models will increasingly run at the edge, enabling real-time analytics without constant connectivity.
Edge Computing in Autonomous Vehicles
Edge computing will be essential for processing gigabytes of sensor data every second.
Cloud–Edge Convergence
Hybrid Cloud/Edge architectures will become standard, with Cloud training AI models and Edge executing them in real time.
Edge Computing is the key to decentralized data processing, enabling instant reactions, improved security, and reduced bandwidth costs—essential for digital transformation and Industry 4.0 success.
Edge does not replace Cloud—it complements it, forming a complete data architecture from edge-level real-time analytics to cloud-level large-scale processing.
Leading Edge Computing Platforms
Stratus Edge Computing Platforms
Stratus’ edge computing platforms are simple, protected, and automated. Designed for operational environments, these platforms are easy to use, scalable, flexible, and reliable, offering plug-and-play solutions that speed up infrastructure transformation. Key advantages include:
- Easy software deployment via virtual machines for multiple sites.
- Faster deployment with standardized, replicable solutions.
- Built-in virtualization and fault tolerance; no special cabling required.
- Industrial-grade design, Class I Division 2 certification, fanless, temperature tolerance from -40 to 60°C, 10–95% humidity, and vibration resistance.
Microsoft Azure IoT Edge
Microsoft Azure IoT Edge is a leading edge computing platform that extends cloud intelligence to edge devices. It enables IoT devices to run Azure services such as AI, analytics, and ML models locally, improving response times and reducing reliance on constant cloud connectivity.
Key features:
- Seamless integration with Azure services.
- Local execution of cloud-powered applications.
- Security features such as device management and encryption.
- Container-based architecture for flexibility.
- Support for diverse devices and ecosystems.
AWS IoT Greengrass
AWS IoT Greengrass supports edge computing for IoT applications, allowing devices to run AWS Lambda functions, process data locally, and sync with the cloud. It also supports real-time data processing and ML inference, making it ideal for low-latency industrial operations.
Key features:
- Local IoT data processing via Lambda functions.
- On-device ML inference.
- Secure communication between edge and cloud.
- Seamless updates and extensibility.
- Offline operation for continuous workflows.
Google Cloud IoT Edge
Google Cloud IoT Edge allows businesses to run AI, ML, and analytics models on edge devices. It speeds up real-time IoT data processing and integrates with Google Cloud services for advanced analytics and long-term storage.
Key features:
- AI and ML capabilities on edge devices.
- Integration with Google Cloud’s analytics and AI suite.
- Real-time data processing and visualization.
- Secure deployment and workload management.
- Container-based applications for portability.
IBM Edge Computing
IBM provides a powerful edge computing platform integrating AI, ML, and data analytics for real-time decisions at the edge. It is used widely in manufacturing, retail, and healthcare.
Key features:
- Real-time analytics for intelligent decision-making.
- Scalable architecture for large IoT deployments.
- Hybrid cloud integration with IBM Cloud.
- AI-powered edge insights.
- Built-in security and compliance features.
Why Choose Stratus Edge Computing Platforms?
Simplicity
Easy Management – Deploying software on Stratus Edge Computing platforms is as simple as loading a solution image onto a virtual machine, making multi-site deployment fast and consistent.
Faster Deployment – Once your solution is fully validated, it can be standardized and replicated easily across sites, plants, or facilities.
Protection
Built-in Virtualization & Fault Tolerance – Stratus platforms come preconfigured with virtualization and fault tolerance, with no need for special hardware pairing or clustering.
Intrinsic Safety & Industrial Grade – ztC Edge is Class I Division 2 certified, fanless, wall- or DIN-mountable, and withstands –40 to 60°C, 10–95% humidity, and 5–500 Hz vibration—ideal for critical applications.
Automation
System Monitoring & Support – Stratus Edge Computing includes 24/7 health monitoring, automated updates and patching, threshold configuration, alerting, log viewing, and predictive issue analysis.
Flexible Management – The ztC™ Advisor tool enables centralized visibility and monitoring of all edge systems, remote troubleshooting, and simplified backup/restore operations.
Explore Stratus Edge Computing Platforms

Optimized for Edge Computing, Stratus ftServer delivers the performance required to support heavy data-processing applications and advanced processors, while ensuring fault tolerance, security, and manageability at the edge of your enterprise network.

Stratus’ newest solution, ztC Edge, is purpose-built for the Edge. It is a secure, ruggedized, highly automated computing platform designed for industrial-grade applications, delivering fast, reliable, efficient performance even in remote, distributed, low-staff environments.
Servo Dynamics – Master Distributor of Penguin Solutions (Stratus Technologies) in Vietnam

Servo Dynamics, the official Master Distributor of Stratus Technologies in Vietnam, provides advanced fault-tolerant Edge Computing solutions for local enterprises. With a mission to deliver continuous availability, seamless integration, and real-time data processing, Servo Dynamics ensures Vietnamese businesses gain access to cutting-edge technologies such as ztC Edge and ftServer.
Servo Dynamics is committed to supporting local industries through expert consulting, seamless implementation, and ongoing support, helping Vietnamese businesses leverage Stratus technologies to compete and grow in today’s data-driven world.

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt