Consulting, Industrial Automation, News
DC Motor Explained – Components, Principle, Applications, and More
DC Motor
A DC motor is an electromechanical device that transforms direct current (DC) electrical energy into mechanical energy through rotation. It harnesses the interaction between magnetic fields to generate a force that spins a rotor within the motor. This rotational motion is then utilized to perform various tasks across different applications.
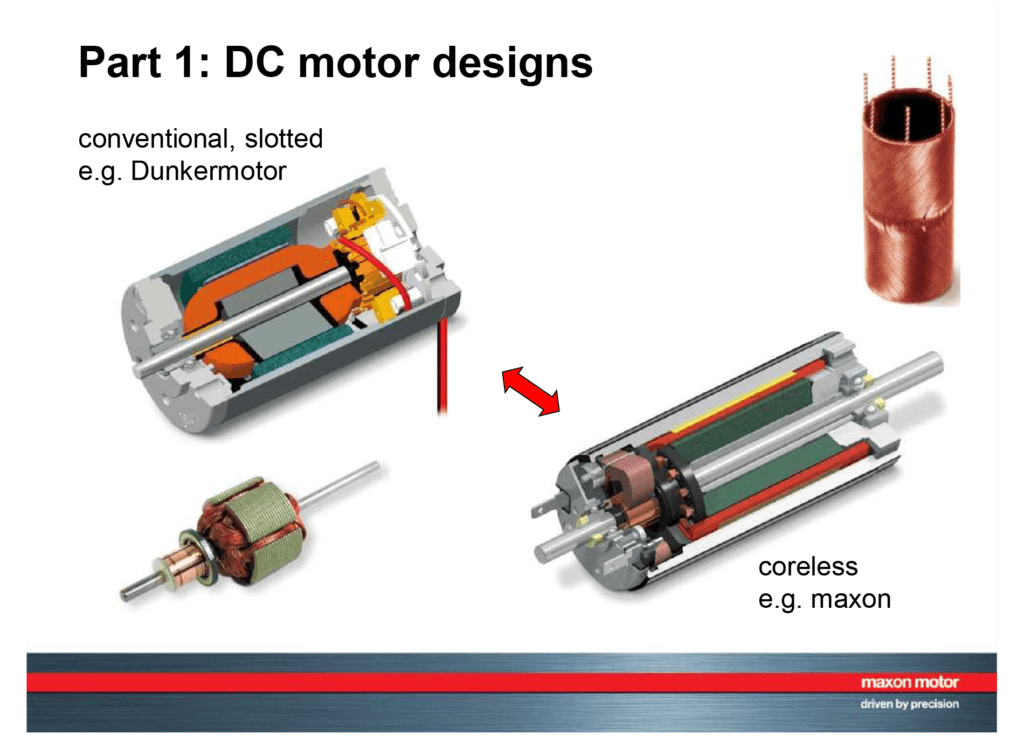
DC Motor Components
The DC motor comprises two primary components:
- Stator: This is the stationary part of the motor, typically housing either permanent magnets or electromagnets.
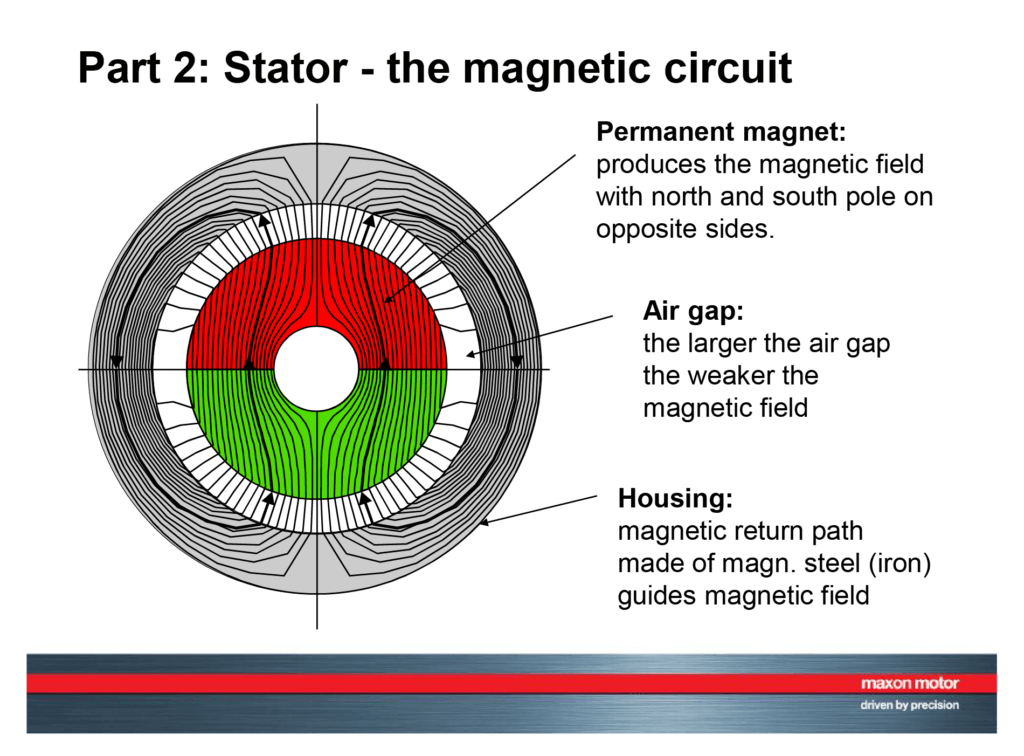
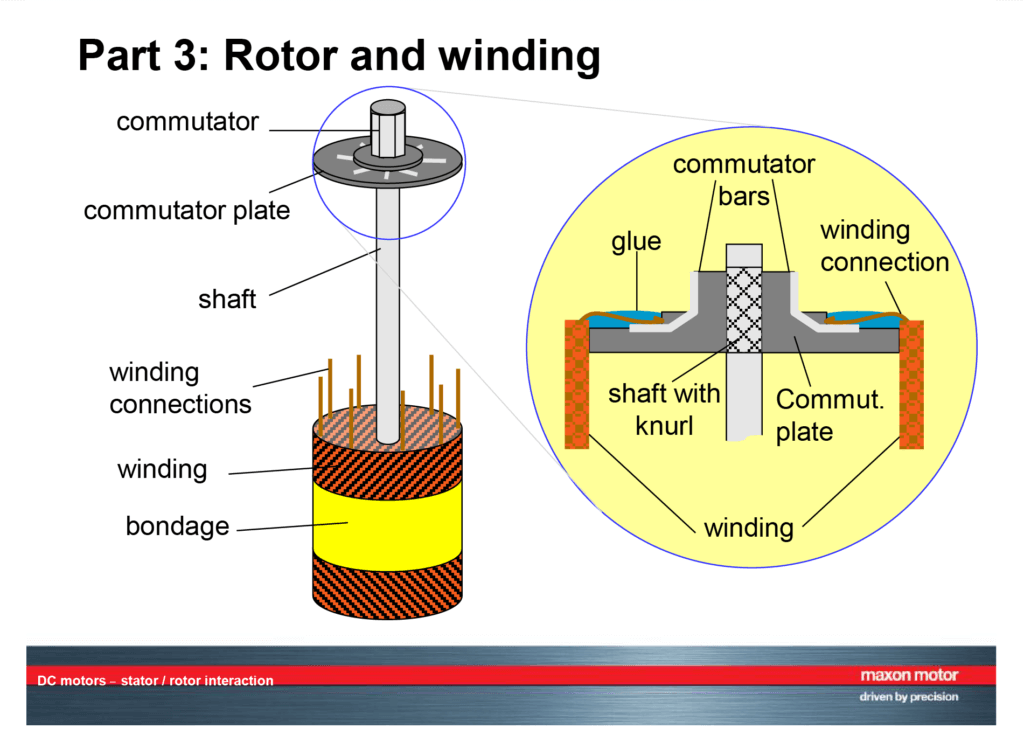
- Rotor: This is the rotating part of the motor, consisting of an armature winding, essentially a coil of wire wound around a core.
How DC Motor works
The basic principle behind the operation of a DC motor relies on a scientific phenomenon called the Lorentz force. This principle states that whenever a current-carrying conductor is placed within a magnetic field, it experiences a mechanical force.
Here’s a breakdown of the operation:
- Current Flow: When a direct current is applied to the armature winding (coil of wire) on the rotor, it generates its own magnetic field.
- Magnetic Interaction: The magnetic field produced by the rotor interacts with the magnetic field of the stator (either permanent magnets or electromagnets).
- Force Generation: This interaction between the two magnetic fields creates a force according to the Lorentz principle.
- Rotational Torque: The generated force acts on the rotor, causing it to rotate. By controlling the direction of the current in the armature winding, you can change the direction of the rotation.
- Speed Control: The speed of the motor’s rotation is directly proportional to the amount of current supplied to the armature winding. More current results in faster rotation, and vice versa.
DC motor advantages
DC motors offer several advantages over their AC counterparts, making them the preferred choice for applications requiring specific functionalities. Here’s a breakdown of some key benefits:
- Superior Speed Control: One significant advantage of DC motors is their exceptional controllability. By adjusting the voltage or current supplied to the armature winding, the motor’s speed can be precisely regulated. This makes them ideal for applications such as robotics, where precise movements are crucial, or for appliances like fans where variable speed settings are desired.
- High Starting Torque: DC motors excel at delivering high torque, particularly during startup. This makes them well-suited for applications requiring quick overcoming of inertia, such as power tools, washing machines, and electric vehicles.
- Simple Construction (Brushed DC Motors): Brushed DC motors, a common type, feature a relatively simple design with fewer components compared to AC motors. This leads to lower manufacturing costs and easier maintenance.
- Less Complex Electronics: While some DC motors may incorporate electronic controls for advanced features, their basic operation often requires simpler electronics compared to AC motors. This can be advantageous for applications prioritizing simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
- Quiet Operation (Brushless DC Motors): Brushless DC motors (BLDC) operate without brushes, eliminating the friction and sparking associated with brushed motors. This results in quieter operation, making them favorable for noise-sensitive environments.
- Efficient at Specific Speeds: DC motors can achieve high efficiency when operated within their optimal speed ranges. This leads to lower energy consumption, making them a suitable choice for applications where energy savings are important.
DC Motor categorize
There are two main ways to categorize DC motors:
- By Stator Field Connection: This classification focuses on how the magnetic field in the stator (stationary part) is generated. Here, there are three main types:
- Brushed DC Motor: This type uses electromagnets in the stator, with windings that receive DC current. It is simple and affordable but requires brush maintenance.
- Shunt DC Motor: Another type with electromagnets in the stator, but the field windings are connected in parallel with the armature (rotor). It offers good speed regulation.
- Series DC Motor: This type also utilizes electromagnets in the stator, but the field windings are connected in series with the armature. It provides high starting torque.
- By Commutation Mechanism: This approach looks at how the current is switched within the motor to maintain rotation. Here, the two main categories are:
- Brushed DC Motor: This type uses physical brushes that make contact with a commutator on the rotor to change current direction.
- Brushless DC Motor (BLDC) or Permanent Magnet DC Motor (PMDC): These motors employ electronic controls to switch current without physical brushes. They offer higher efficiency and lifespan compared to brushed motors.
While the first categorization (by stator field connection) is more traditional, the second one (by commutation mechanism) is becoming increasingly common. Brushless DC motors (BLDC) and Permanent Magnet DC Motors (PMDC) essentially represent the same technology, with PMDC being a simpler version without some of the advanced features of BLDC motors.
The difference between AC & DC Motor
The primary distinction between AC and DC motors lies in the type of current they utilize and how they generate rotation:
- Current Type:
- AC Motor: Runs on Alternating Current (AC) where the current periodically reverses direction. This is the type of electricity delivered through household outlets.
- DC Motor: Functions on Direct Current (DC), where the current flows in only one direction. This is the form of power typically obtained from batteries.
- Magnetic Field & Rotation:
- AC Motor: The stator (stationary part) generally contains electromagnets. The alternating current continually switches the polarity of the magnetic field in the stator, inducing a rotating magnetic field in the rotor (rotating part). This interaction between the rotating magnetic fields generates torque, spinning the rotor.
- DC Motor: The stator typically features permanent magnets or electromagnets with a constant magnetic field. When DC current is applied to the rotor’s coil (armature winding), it creates its own magnetic field. The interaction between the constant stator field and the rotor’s magnetic field produces torque for rotation. In some DC motors, brushes and a commutator are utilized to switch the current in the rotor, ensuring continuous rotation.
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences:
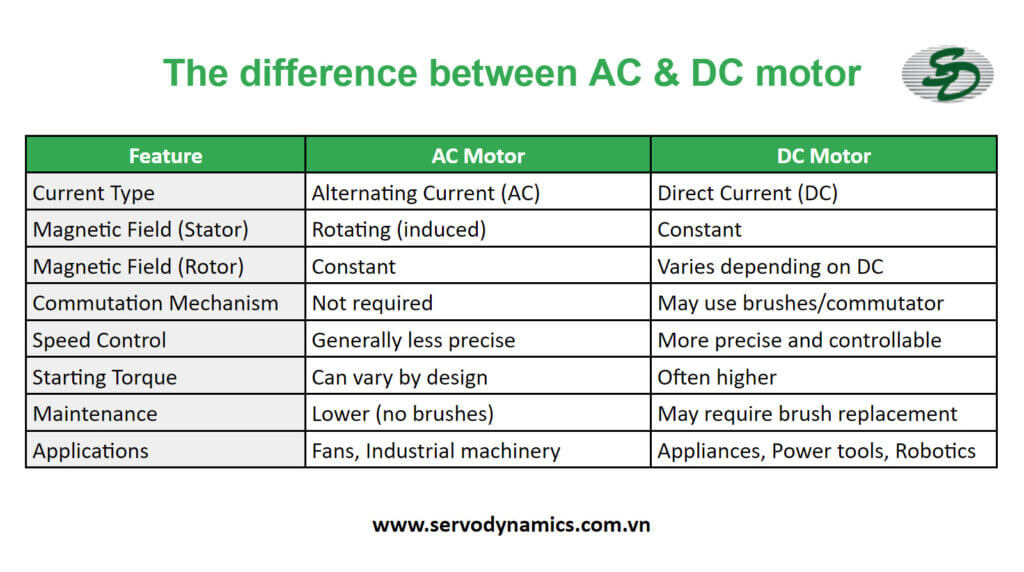
In essence:
- AC motors are simpler in design, require less maintenance, and are generally preferred for constant speed applications where high starting torque is not essential.
- DC motors, on the other hand, offer more precise speed control, making them suitable for variable speed applications. They often provide higher starting torque but may require brush maintenance, depending on the type.
DC Motor Applications
DC motors find uses in a wide variety of applications due to their versatility, controllability, and range of available sizes and power outputs. Here’s a breakdown of some common applications categorized by their typical DC motor requirements:
High Starting Torque:
- Power Tools: Drills, saws, sanders, and other power tools benefit from the high starting torque of DC motors to quickly overcome inertia and begin working.
- Appliances: Vacuum cleaners and washing machines utilize DC motors for their high initial torque to handle heavy loads.
- Transportation: Electric vehicles, like scooters and some hybrid cars, employ DC motors for their ability to deliver high torque during startup and acceleration.
Variable Speed Control:
- Consumer Electronics: Fans, DVD players, and other home appliances use DC motors where precise speed control is desirable.
- Industrial Machinery: Production lines and automated processes often rely on DC motors for adjustable speed control to match specific application requirements.
- Robotics: Robots utilize DC motors in their joints for controlled and maneuverable movements.
Continuous Duty Applications:
- Cooling Systems: Computer fans and air conditioners employ DC motors for their reliable and continuous operation in keeping systems cool.
- Medical Equipment: Medical devices like dialysis machines and treadmills benefit from the consistent performance of DC motors.
- Office Equipment: Printers and copiers utilize DC motors for their ability to handle long periods of operation.
Small Size and Low Power:
- Toys and Hobby Products: Remote-controlled cars, drones, and other hobbyist items use small DC motors for their compact size and efficient power consumption.
- Printers and Scanners: These devices rely on small DC motors to move components with precision.
- Medical Devices: Some medical devices, like insulin pumps, incorporate tiny DC motors for quiet and controlled operation.
This is not an exhaustive list, but it highlights the diverse applications of DC motors across various industries and everyday products. Their ability to convert electrical energy into controllable mechanical rotation makes them a fundamental building block in many technological advancements.
Finding the Right DC Motor
Selecting the most suitable DC motor for your project involves careful consideration of several key factors. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown to guide you through the process:
- Identify Application Needs:
- Speed: Determine the required rotation speed of the motor (RPM).
- Torque: Assess the necessary twisting force (torque) for your project.
- Voltage: Specify the DC power source voltage (e.g., 12V battery, 24V power supply).
- Duty Cycle: Consider the duration and frequency of motor operation (intermittent vs. continuous use).
- Size Constraints: Evaluate any limitations on the physical dimensions or weight of the motor for your application.
- Motor Specifications:
- Research DC motors that meet or exceed your project’s requirements for speed, torque, voltage, and size.
- Review manufacturers’ datasheets, which provide detailed specifications for each motor model.
- Motor Type Selection:
- Brushed DC Motors: Simple and cost-effective, offering high starting torque. However, they require brush maintenance and have a shorter lifespan.
- Brushless DC Motors (BLDC): More efficient and quieter than brushed motors, with a longer lifespan. Generally, they are more complex and expensive.
- Permanent Magnet DC Motors (PMDC): Efficient and quiet, similar to BLDC motors but simpler in design. They may have a lower torque output compared to brushed DC motors.
- Additional Considerations: Beyond the core specifications, consider these factors:
- Duty Cycle: Ensure the motor’s duty cycle rating aligns with your application’s usage requirements.
- Controllability: If precise speed control is essential, consider motors compatible with motor controllers.
- Cost: Balance the motor’s features and price with your project’s budgetary constraints.
By following these steps and considering all relevant factors, you can confidently choose the right DC motor for your project.
maxon DC motor
Maxon DC motors are high-precision DC motors designed for applications that require exceptional performance, reliability, and durability. They are manufactured by Maxon Group, a Swiss company founded in 1961 that specializes in electric motors, drives, and control systems.
Maxon DC motors come in a variety of brushed and brushless DC motor options, each designed to meet the specific needs of a particular application. Brushed DC motors are known for their simple design, low cost, and high starting torque. Brushless DC motors offer higher efficiency, longer lifespans, and lower maintenance requirements compared to brushed DC motors.

Here are some of the key benefits of using Maxon DC motors:
- High power density: Maxon DC motors offer a high ratio of power output to motor size, making them ideal for applications where space is limited.
- Long lifespan: Maxon DC motors are built with high-quality materials and components, and they are designed to last for many years of operation.
- Low noise operation: Brushless DC motors are particularly quiet due to the absence of brushes and commutators.
- Wide range of speeds and torques: Maxon DC motors are available in a wide range of speeds and torques to meet the specific needs of your application.
- Precise speed control: Maxon DC motors can be precisely controlled using a variety of methods, such as pulse width modulation (PWM).
- High efficiency: Maxon DC motors are designed to be energy efficient, which can help to save on operating costs.
Maxon DC motors are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Medical devices: Maxon DC motors are used in a variety of medical devices, such as insulin pumps, surgical robots, and prosthetics. Their reliability, precision, and quiet operation make them ideal for these critical applications.
- Industrial automation: Maxon DC motors are used in a variety of industrial automation applications, such as robotics, assembly lines, and material handling. Their high power density, long lifespan, and precise speed control make them well-suited for these demanding applications.
- Aerospace and defense: Maxon DC motors are used in a variety of aerospace and defense applications, such as drones, satellites, and missiles. Their ability to withstand harsh environments and their high reliability make them essential for these applications.
- Consumer electronics: Maxon DC motors are also used in a variety of consumer electronics, such as high-end audio equipment, cameras, and drones. Their quiet operation and smooth speed control make them ideal for these applications.
If you are looking for a high-precision, high-performance DC motor for your application, then a Maxon DC motor is a great option to consider. However, they tend to be more expensive than some other options on the market.
Servo Dynamics: Your Partner for High-Precision Maxon Motors in Vietnam
Located in Vietnam, Servo Dynamics is the authorized distributor for Maxon, a world-renowned manufacturer of high-precision DC motors, drives, and control systems. This partnership allows Vietnamese businesses and individuals to access Maxon’s cutting-edge technology directly within the country.
As the authorized distributor, Servo Dynamics brings Maxon’s technology to Vietnam, along with additional benefits:
- Local Support: Servo Dynamics provides technical expertise and application know-how to help you select the most suitable Maxon solution for your project.
- Simplified Acquisition: With Servo Dynamics, you can acquire genuine Maxon products efficiently without the need for complex international transactions.
- Potential After-Sales Support: Depending on Servo Dynamics’ offerings, you may benefit from local after-sales support and maintenance services for your Maxon motors.
Considering Maxon for your project?
If your project demands high-precision motion control, exceptional reliability, and a wide range of options, then Maxon DC motors are a perfect choice. Servo Dynamics, as the authorized distributor, can be your trusted partner in Vietnam to help you acquire the ideal Maxon solution and potentially provide valuable local support.
Contact us now!
[formidable id=”1″]Contact Information
Thanks for visiting our website. For more information, please contact:
Servo Dynamics Engineering Co., Ltd
Tel: +84 28 3740 2128
Email: sales@servodynamics.com.vn
Website: www.servodynamics.com.vn
Official Account Zalo: Servo Dynamics Engineering
Saigon
4/1B Luong Dinh Cua Str., An Khanh Ward, Thu Duc City, HCMC, Vietnam
Tel: (84-28) 3740 2128
Fax: (84-28) 3740 2129
Da Nang
120 Xo Viet Nghe Tinh, Hoa Cuong Nam Ward, Hai Chau District, Da Nang, Vietnam
Tel: (84-23) 6361 1128
Ha Noi
Unit 05, 15th Floor, Han Viet Tower, 203 Minh Khai Street, Hanoi, Vietnam
Tel: (84-24) 3632 1617
Fax: (84-24) 3632 1618

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt