Consulting, Industrial Automation, News, Solutions
What is an Industrial Electrical Cabinet? Structure, Types, & Selection Guide
The industrial electrical cabinet serves as the backbone for controlling, protecting, and distributing electrical power in industrial systems. This article provides a comprehensive overview, from basic concepts and detailed structure to common types, current 2025 pricing, and selection guidelines. Discover now to choose the optimal solution for your business!
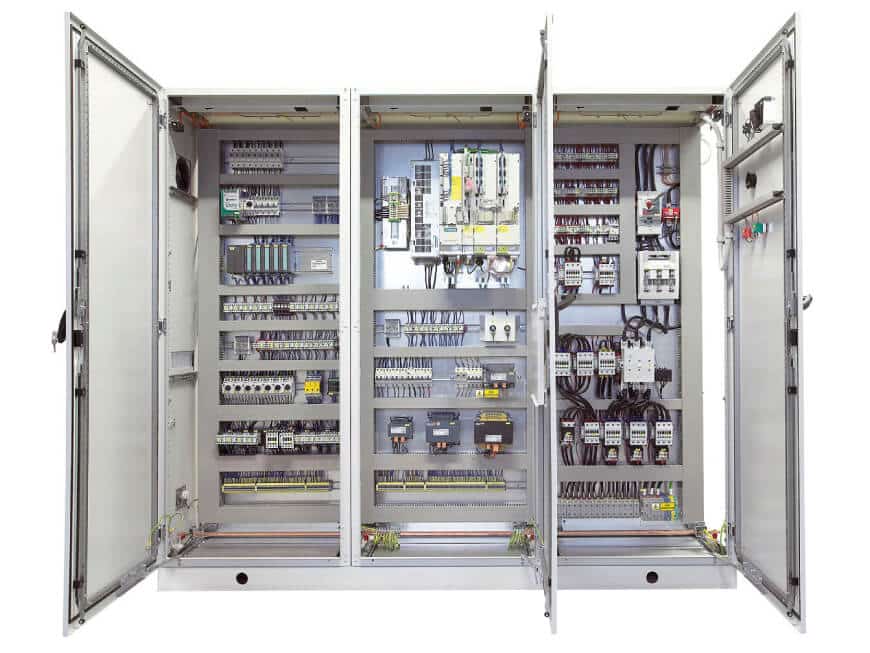
What is an Industrial Electrical Cabinet?
Industrial Electrical Cabinet Concept
An Industrial Electrical Cabinet is a box-shaped structure, typically made of metal (steel or stainless steel), used to enclose, protect, and organize electrical equipment and control circuits.
It is installed in production areas, construction sites, or large infrastructure facilities where there is a need for high-capacity electrical power distribution and usage.
Functions and Role in the Electrical System
The industrial electrical cabinet performs several essential roles, including:
- Power Distribution: Receives power from the substation (or main source) and divides it among branch circuits and loads (motors, machinery, lighting systems).
- System Protection: Protects circuits and equipment from dangerous faults such as short circuits, overloads, overvoltage, and leakage current, preventing damage and fire hazards.
- Control and Operation: Houses control devices (PLC, relays, contactors) to automate or allow operators to start, stop, or adjust industrial equipment as required.
- Measurement and Monitoring: Equipped with meters, indicator lights, or HMI/SCADA screens to measure electrical parameters (Amps, Volts, frequency, power) and monitor the operational status of the system.
What does an Industrial Electrical Cabinet consist of?
An industrial electrical cabinet is a combination of two main components:
- Cabinet Enclosure: The outer protective shell, which determines the size, protection level (IP rating), and environmental resistance.
- Electrical Equipment: The internal components and electrical apparatus that perform distribution, protection, and control functions.
Structure of the Industrial Electrical Cabinet
The cabinet is structured from the following core parts, working synchronously to form a complete system:
Cabinet Enclosure (Size – Material – IP Rating)

The enclosure is the most critical component, acting as “armor” to protect sensitive electrical devices.
- Material: Most common are Powder-coated steel sheets (reasonable cost, high mechanical durability) and Stainless steel (corrosion-resistant, often used in humid or food-grade environments).
- Size: Highly diverse, ranging from small wall-mounted cabinets (H x W: 400x300mm) to large floor-standing cabinets (Height 2200mm, Width 1000mm), depending on the amount of equipment to be installed.
- IP Rating (Ingress Protection): An international standard (IEC) assessing the cabinet’s resistance to the ingress of solids (dust) and liquids (water).
- IP20: Typically used indoors, in dry environments.
- IP43: Protects against solid objects and light water spray.
- IP54/IP55: Completely dust-protected, resistant to water jets/light pressure water (suitable for factory installation).
- IP65/IP66: Completely dust-tight, resistant to high-pressure water (essential for outdoor electrical panels).
Internal Equipment
These devices are scientifically arranged on DIN rails and connected by busbars and conductors.
- Electrical Apparatus (CB, MCCB, contactor, etc.):
- CB/MCB (Circuit Breaker): Miniature circuit breaker, used for overload and short-circuit protection in low-current circuits.
- MCCB (Moulded Case Circuit Breaker): Used as a main disconnecting switch, protecting high-current circuits.
- Contactor (Magnetic Starter): High-load switching device, used to control motors remotely.
- Thermal Relay: Protects the motor from prolonged overloads.
- Busbars and Conductors:
- Busbar: The main electrical conductor, made of copper or aluminum, used for conducting and distributing large currents within the cabinet.
- Conductors/Wiring: Used to connect auxiliary loads.
- Control Devices – PLC – Relays:
- PLC (Programmable Logic Controller): The “brain” of the cabinet, executing complex automation programs.
- Interposing/Time Relays: Used in simple control circuits or for performing time-delay tasks.
- VFD (Variable Frequency Drive/Inverter): Adjusts the speed of AC motors, saving energy and precisely controlling the production line speed.
- Cooling Equipment (Fans, Cabinet AC units, etc.):
- Ventilation Fans: Help circulate air, expelling hot air outside.
- Cabinet Air Conditioner/Heat Exchanger: Used for cabinets with high equipment density, high heat generation, or installed in high-temperature environments (helps maintain stable temperature, protecting component lifespan).
Cabinet Accessories
Accessories ensure stable operation and convenience for maintenance:
- Hinges and Locks: Ensure the cabinet door seals tightly, providing dust and water resistance, and security.
- Cabinet Light – Fan: Light serves for maintenance work; fans serve for cooling.
- Cabinet Base – Mounting Rails – DIN Rail: The base helps stabilize floor-standing cabinets; the DIN rail is a standard metal track used to mount control devices (CB, contactor, relay).
Common Types of Industrial Electrical Cabinets
Industrial electrical cabinets are classified by various criteria, making it easier to select the right type for each application.
By Function
| Cabinet Type | Primary Function | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Main Distribution Board (MSB/DB) | Divides main power source from the substation to auxiliary loads. | Buildings, industrial parks, substations. |
| Control Panel | Contains PLC, VFD, HMI to automatically control pumps, compressors, conveyors, and production processes. | Production lines, HVAC systems, water treatment. |
| ATS Cabinet (Automatic Transfer Switch) | Automatically switches power between the main source and the backup source (generator). | Hospitals, data centers, hotels. |
| Power Factor Correction (Capacitor Bank) | Improves power factor (cos phi), reducing electricity costs and energy loss. | Factories using many motors (inductive loads). |
| Motor Control Center (MCC) | Centralized control and protection for multiple motors within a plant. | Large manufacturing plants (Cement, Steel, Textile). |
By Design
- Floor Standing: Large size, typically the main switchboard (MSB) or MCC, placed independently on the floor.
- Wall Mounted: Compact size, often a branch distribution board (DB) or local control panel, mounted on the wall.
- Flush Mounted: Installed recessed into the wall, only exposing the control face, often used in buildings requiring high aesthetics.
- Single-door – Double-door – Modular: Depending on size and purpose, the cabinet may have a single opening door, double doors (for large cabinets), or be divided into separate compartments (modular MCC cabinets).
By Installation Environment
- Outdoor Electrical Cabinet: The enclosure must meet a minimum IP protection level of IP55 or IP66, including a canopy, watertight rubber gasket, and possibly UV-resistant paint.
- Waterproof – Dustproof Cabinet (IP rated): Cabinets with high IP ratings (like IP65) use special door gaskets and sealed penetration components.
- Portable/Mobile Cabinet: Usually small, with wheels or handles, used on construction sites or temporary events.
Applications of Industrial Electrical Cabinets
Industrial electrical cabinets are an indispensable part of every large-scale power system:
- Manufacturing Plants: Controlling production lines, pumps, compressors, industrial fans, furnaces, and automation systems.
- Construction Sites: Main power distribution cabinets, temporary socket distribution boards.
- Buildings – Commercial Centers: MSB main distribution panel, DB floor distribution panel, ATS for elevators and emergency lighting.
- Pumping Stations – HVAC Systems: Control panels for domestic water pumps, fire fighting pumps, and ventilation/air conditioning control systems.
- Automation Lines: Containing PLCs, VFDs, Servo Drives to control robots and precision machinery.
Drawings – Diagrams – Industrial Cabinet Design
The design of the electrical cabinet always starts with technical drawings to ensure safety and accurate operation.
Types of Cabinet Drawings (DWG, PDF)
A standard set of electrical cabinet design documents typically includes:
- Schematic Diagram (Sơ đồ nguyên lý): Illustrates the operational principle of the equipment, control circuits, and logical connections between components (often in PDF or DWG format).
- Layout Diagram (Sơ đồ bố trí thiết bị): Shows the physical location of equipment inside the cabinet, aiding installation and maintenance.
- Wiring Diagram (Sơ đồ đấu nối): Details the terminals, wire numbers, and wire colors connecting the devices.
How to Read Industrial Electrical Cabinet Drawings
To read the electrical cabinet drawing, you need to be familiar with:
- Symbol Recognition: Understand the meaning of device symbols (CB, Contactor, Relay, PLC, Motor).
- Reading the Control Circuit: Follow the current flow from the source through push buttons, relays, and the PLC to the executing device (Contactor coil).
- Reading the Power Circuit: Follow the power current from the main source through the CB to the loads (Motor).
Common Symbols in Electrical Cabinets
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| CB/Q | Circuit Breaker (Aptomat) |
| KM | Contactor (Khởi động từ) |
| OL/F | Thermal Overload Relay (Rơ le nhiệt) |
| H | Indicator Lamp (Đèn báo) |
| S | Push Button (Nút nhấn) |
| X | Terminal Block (Hộp đấu dây) |
Safety Standards in Design (IEC, TCVN)
Electrical cabinet design must strictly comply with safety standards:
- IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission): A set of international standards for electrical equipment, particularly IEC 61439 (Standard for Low-Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear Assemblies) and IEC 60529 (IP Rating codes).
- TCVN (Vietnam National Standards): National standards applied based on IEC.
- Safety Clearance: Ensure electrical clearance and creepage distances between busbars and equipment according to regulations.
Installation – Construction – Wiring Procedures
The standard installation procedure ensures the cabinet operates safely, reliably, and is easy to maintain.
Standard Cabinet Installation Procedure
- Preparation: Check drawings, materials, tools, and the installation area.
- Enclosure Fabrication: Install DIN rails, cable trays, ventilation holes, and the cabinet base.
- Equipment Mounting: Secure devices (CB, Contactor, PLC) onto the DIN rail/mounting panel according to the layout diagram.
- Wiring: Perform wiring for the power circuit and control circuit according to the wiring diagram. Wires must be numbered and neatly routed in cable trays.
- Inspection & Testing: Check the tightness of connections, measure continuity, test insulation, and perform no-load running tests.
- On-site Fixing: Install the cabinet at the location (wall-mounted or floor-standing), and connect the incoming/outgoing power cables.
How to Wire Single-phase and Three-phase Cabinets
- Single-phase Cabinet: Simple wiring, uses 1 phase conductor (L) and 1 neutral conductor (N).
- Three-phase Cabinet: The power circuit uses 3 phase conductors (L1, L2, L3) and may include a neutral (N) and ground (PE) conductor. Three-phase wiring must ensure load balancing among the phases.
Common Wiring Errors
- Loose Connections: Leads to heat generation, fire risk, or voltage drop.
- Incorrect Phase Sequence: Causes motor damage (reverse rotation).
- Mixing Control/Power Wires: Damages the control circuit.
- Lack of Grounding: Fails to ensure operator safety.
Maintenance – Cleaning – Periodic Inspection Guide
Periodic maintenance helps extend lifespan and reduce accident risk:
- Temperature Check: Monitor the internal temperature of the cabinet.
- Cleaning: Vacuum dust and wipe down the inside of the cabinet (must be powered off before cleaning).
- Tightening Screws: Re-torque all terminals, especially at the busbars and contactors, as they may loosen due to vibration and thermal expansion.
- Measurements: Measure insulation, load current, and voltage.
- Protection Device Check: Test the operation of Circuit Breakers and Thermal Relays.
How Much Does an Industrial Electrical Cabinet Cost? (Reference Price)
The average price for a standard industrial electrical cabinet (using genuine equipment, IP54 powder-coated steel enclosure) typically ranges from 8,000,000 VND to 150,000,000 VND, depending on the type (control or distribution) and capacity.
- Note: This is a reference price and may change depending on the time, detailed technical requirements of the project, and the supplier.
How to Choose the Right Industrial Electrical Cabinet
To ensure safety, efficiency, and optimal cost, the selection of the electrical cabinet must be carefully considered.
Choose by Electrical Load – Purpose of Use
- Main Distribution: Choose an MSB cabinet, using high-breaking capacity ACB (Air Circuit Breaker) or MCCB.
- Motor Control: Choose a control panel, requiring Contactors, Thermal Relays, and possibly a VFD if speed adjustment is necessary.
- Continuous Protection: Choose an ATS cabinet if the power supply is not allowed to be interrupted (e.g., hospitals, data centers).
Choose by IP Standard – Operating Environment
| Environment | Recommended IP Rating |
|---|---|
| Office, dry technical room | IP20 – IP30 |
| Indoor factory production area (with dust) | IP43 – IP54 |
| Washing, food areas (with water) | IP55 – IP65 |
| Outdoor, under rain/sun | IP65 – IP66 (with canopy) |
Comparing Budget Cabinets and High-Standard Cabinets
| Factor | Budget Cabinet | High-Standard Cabinet |
|---|---|---|
| Enclosure | Thin steel, easily warped, low IP rating, poor powder coating. | Thick steel/Stainless steel, high IP rating (sealed gasket), precise fabrication. |
| Components | Non-genuine/unknown origin, prone to fire/explosion, short lifespan. | Reputable brands (ABB, Schneider), with CO/CQ, durable operation. |
| Safety | Risk of leakage, missing busbars, poor connections, non-compliant with TCVN/IEC. | Compliant with insulation standards, professional installation, absolute safety. |
Notes When Purchasing an Industrial Electrical Cabinet
- Request Documents (CO/CQ): Ensure the electrical equipment is genuine.
- Check Test Report: Require the manufacturer to provide reports on durability and overload capacity testing before acceptance.
- Assess Installer Expertise: The installation unit must have experience and a highly qualified engineering team.
Common Industrial Electrical Cabinet Samples
Control Panel – Distribution Board Samples
Electrical control panel for a Fire Fighting Pumping system (IP54, installed indoors). DB floor electrical distribution board (wall-mounted, aesthetic, IP43).
Waterproof Outdoor Cabinet Samples
ATS electrical cabinet for outdoor pumping station (IP66, with canopy and base).
Custom Order Cabinet Samples
Modular MCC cabinet, with draw-out type compartments allowing quick replacement during maintenance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the English term for Tủ điện công nghiệp?
The term “Tủ điện công nghiệp” in English is referred to as Industrial Electrical Cabinet or Electrical Panel (general), Control Panel (for control), and Switchgear (for switching and protection gear).
How many types of industrial electrical cabinets are there?
There are many classification methods, but the 4 most common types based on function are: Distribution Cabinet (MSB/DB), Control Cabinet, ATS Cabinet (Transfer Switch), and Capacitor Bank.
Should I use a steel or stainless steel enclosure for the cabinet?
- Powder-coated steel enclosure: Suitable for indoor, dry environments, low cost, easy to fabricate.
- Stainless steel (304 or 316) enclosure: Mandatory for harsh environments, high humidity, chemicals, food processing, or areas requiring high sanitation.
What IP rating is required for an outdoor electrical cabinet?
Outdoor electrical cabinets must have a minimum protection level of IP55, but IP65 or IP66 is recommended to ensure complete dust protection and resistance to strong water jets or heavy rain.
When is a cabinet air conditioner or cooler needed?
A cabinet air conditioner or heat exchanger is needed when:
- The ambient temperature is too high (above 40 degrees C).
- The equipment density in the cabinet is too high, especially devices generating significant heat like VFDs or Servo Drivers.
- The cabinet contains sensitive electronic devices (PLC, HMI) that require maintaining a stable temperature to ensure their lifespan.

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt