Consulting
ToF Sensors: How They Work
What Are ToF Sensors?
Ever wondered how a camera on your phone can blur the background of a photo so perfectly? Or how a robot vacuum cleaner expertly navigates around your furniture? The technology behind these feats is often a Time-of-Flight (ToF) sensor.
In simple terms, a ToF sensor is a device that measures the distance between itself and an object by using a pulse of light. It works on a simple principle: the sensor emits a brief, invisible light pulse (usually from a laser or an LED) and then times how long it takes for that light to travel to the object and bounce back. Because the speed of light is a constant, the sensor can quickly and accurately calculate the distance to the object.
This concept is similar to how an echo works. When you shout in a canyon, the time it takes for the sound to return tells you how far away the opposite wall is. A ToF sensor does the same thing, but with light and with incredible precision, providing real-time data about its surroundings.
How ToF Compares to Other Imaging Techniques
ToF is just one of several methods used to capture 3D information. Two other common techniques are:
- Stereo Cameras: These systems mimic human vision by using two separate lenses. The slight differences in the images captured by each lens are used to calculate depth and distance, just like our brains do to create 3D perception.
- Structured Light Imaging: This method projects a known pattern, like a grid, onto an object. By analyzing how the pattern is distorted on the object’s surface, the system can determine its shape and distance.
Each of these technologies has unique strengths and weaknesses. A major benefit of ToF is that it’s an “active” imaging technique, meaning it provides its own light source. This allows it to work effectively even in complete darkness, unlike passive systems such as stereo cameras that require external light. However, ToF sensors can face challenges in very bright natural surroundings, such as direct sunlight, as the sun’s light can interfere with the sensor’s own light waves. They also struggle with highly reflective or “shiny” surfaces and in corners, which can create multiple light reflections and confuse the sensor.
The Two Main Types of ToF Sensors
While the core principle is the same, ToF sensors come in two primary types, based on the type of wave they use:
- Optical ToF Sensors: These are the most common type and use a pulse of light, typically in the infrared (IR) range, for distance measurement. The light pulse is emitted, reflects off the object, and is detected by the sensor. The distance is then calculated based on the travel time and the speed of light.
- Electromagnetic ToF Sensors: These sensors use electromagnetic waves, such as radar or lidar. The principle is identical to optical sensors: a wave is emitted, it reflects off the object, and the travel time is measured to calculate the distance.
Applications of ToF Sensors
Because they are highly accurate and versatile, ToF sensors are integrated into countless products and systems we use every day. Here are ten major applications:
- Robotics: ToF sensors are critical for obstacle detection and navigation. They allow robots, from a Roomba vacuum to sophisticated models like Atlas from Boston Dynamics, to sense their environment and plan their movements.
- Security: These sensors are utilized in various security systems to detect movement and the presence of intruders, triggering alarms or activating surveillance cameras.
- Automotive: They are a core component of driver-assistance systems in modern vehicles. Features like adaptive cruise control and collision avoidance systems rely on ToF sensors to measure the distance to other vehicles and objects, helping to prevent accidents.
- Medical: ToF technology is used for non-invasive imaging, such as in Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), which produces high-resolution images of body tissues for diagnostics.
- Industrial: In factories and warehouses, ToF sensors are essential for industrial automation. They are used for material handling, positioning objects on conveyor belts, and guiding autonomous vehicles to prevent collisions.
- Consumer Electronics: These sensors are found in our everyday devices. Smartphones use them for facial recognition and biometric authentication, while tablets and laptops can use them for gesture recognition.
- Drones: Drones equipped with ToF sensors can be used to map crops and estimate yield in agriculture, helping farmers manage their resources more efficiently and reduce chemical usage.
- Retail: Retailers use ToF sensors to track customer movements, analyze buying patterns, and monitor inventory levels. This data helps them optimize store layouts and provide a better shopping experience.
- Surveying: In the field, surveyors use ToF sensors for topographic mapping and land measurement, accurately measuring distances to buildings, trees, and other landmarks.
- Gaming: ToF sensors revolutionized the gaming industry by tracking player movements. Devices like the Nintendo Wii and Xbox Kinect used this technology to create a more immersive and interactive gaming experience.
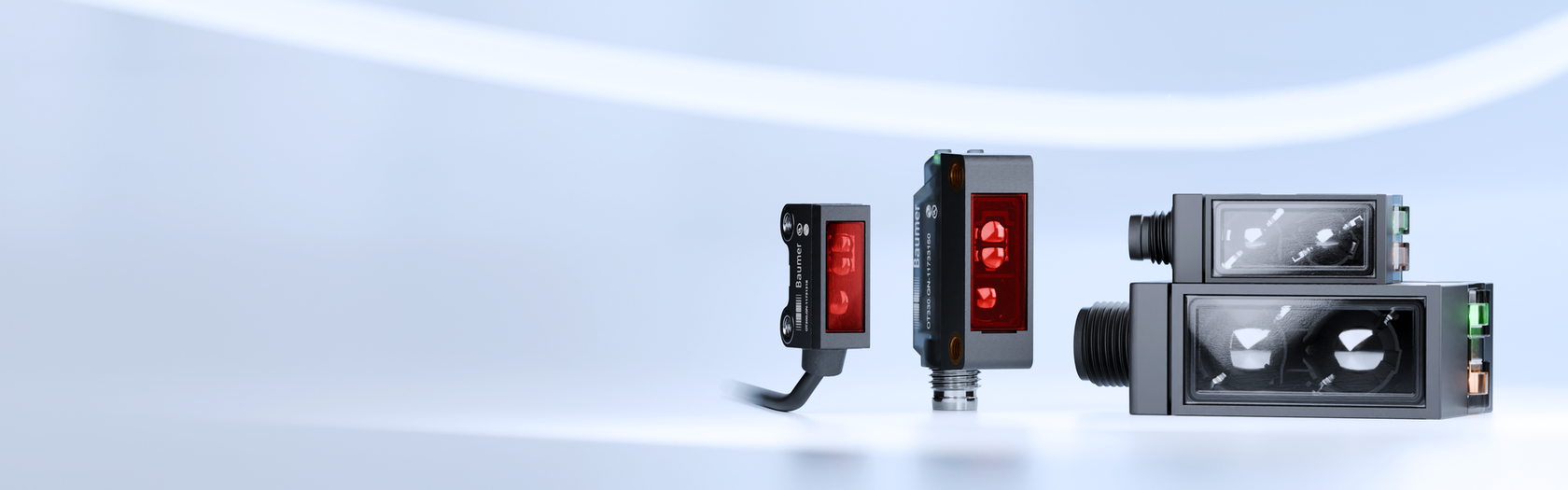

Advancements in ToF Technology: A Look at Baumer’s Sensors
Companies like Baumer are at the forefront of innovation in ToF technology. Their new sensors, the OT200 and OT330, are a perfect example of this progress. These models combine high performance with an incredibly small form factor.
The OT200, for instance, is the most compact ToF sensor on the market, yet it boasts the smallest blind zone and a long range of up to 2 meters. The slightly larger OT330 offers a range of up to 2.5 meters. Both sensors are designed for easy installation and low maintenance, reducing the overall cost of ownership.
These new sensors also use infrared lasers, which are less affected by factors like color, surface texture, and ambient light compared to other light sources. This makes them highly reliable in diverse environments, from dusty factory floors to complex intralogistics systems.
In essence, ToF sensors are an efficient and reliable solution for measuring distances and capturing real-time data, and their ongoing development ensures they will continue to play a crucial role in shaping a wide range of industries for years to come.
Servo Dynamics Engineering: Authorized Distributor of Baumer Sensors in Vietnam
As a leading provider of advanced industrial solutions, Servo Dynamics Engineering is proud to be the authorized distributor of Baumer products in Vietnam. We offer a comprehensive portfolio of Baumer’s cutting-edge sensors, including the new OT200 and OT330 Time-of-Flight sensors, providing our customers with access to the highest quality and most innovative technology on the market.
At Servo Dynamics Engineering, we don’t just supply products—we provide expertise. Our team of specialists is dedicated to helping you find the perfect ToF sensor solution for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Whether you’re working in manufacturing, logistics, or automation, we are committed to supporting your business with reliable technology and exceptional service.
Explore Baumer Products
Learn more

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt