Consulting
Distance Sensor: Principle, Structure, and Detailed Applications
The Distance Sensor (or Distance Measuring Sensor) is one of the most critical non-contact measurement devices in industrial automation, robotics, and smart technology. They act as the “eyes,” providing accurate distance data, helping machinery with positioning, motion control, dimension measurement, and ensuring operational safety in various environments.
If you are researching what a distance sensor is, its operating principle, or common types of laser distance sensors, this article will provide a comprehensive and in-depth view, from their structure and classification to the necessary technical factors for effective selection and implementation.
What is a Distance Sensor?
Concept of Distance Sensors
A Distance Sensor (English name: Distance Sensor or Distance Measuring Sensor) is an electronic device that converts physical distance information from the sensor to a target object into a measurable and processable electrical signal.
This measurement process is non-contact, which helps protect the surface of the object and ensures the sensor’s lifespan in harsh or high-speed environments.
The distance information is subsequently converted into standard signals:
- Analog (Continuous Signal): Typically 4-20mA or 0-10V, corresponding to the sensor’s minimum and maximum measurement range. The Analog signal allows the control system (like a PLC) to know the exact position of the object within the measuring range.
- Digital (Discrete Signal): Usually ON/OFF (PNP or NPN), used to detect an object when it enters or crosses a fixed distance threshold (Switching Point).
Advanced Functions & Role in Industry 4.0
In the modern industrial environment, the role of distance sensors goes far beyond simple measurement:
- Quantitative Measurement: Provides the absolute distance value in units (mm, cm, m) with high resolution.
- Closed-Loop Control: Accurate distance data is used to control the speed, position, or tension of automated systems (e.g., controlling material thickness).
- Dimensional Measurement: Measures thickness, outer/inner diameter (OD/ID), or checks the flatness of products during manufacturing.
- Smart Automation: In Industry 4.0 and IoT systems, distance sensors with digital communication (IO-Link, Ethernet) provide remote diagnostic and calibration data, enhancing predictive maintenance efficiency.
Distinguishing Distance Sensors from Proximity Sensors
| Feature | Distance Sensor | Proximity Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Analog (4-20mA/0-10V) or Digital. | Digital (ON/OFF) fixed. |
| Information Provided | Continuous distance value (e.g., 100 mm, 101 mm, … 500 mm). | Only presence/absence state (ON/OFF) when the object is within the sensor’s range. |
| Primary Purpose | Measurement of position, dimension, or level. | Detection of an object’s presence or absence. |
| Technology | Laser ToF, Ultrasonic, Infrared Triangulation, Radar. | Inductive, Capacitive, Photoelectric. |
In summary, a proximity sensor operates merely as a switch activated at a fixed point, while a distance sensor functions as an electronic ruler.
Structure and Operating Mechanism of Distance Sensors
Despite employing various technologies, all distance sensors adhere to the basic principle of transmitting energy and receiving reflected energy.
Emitter and Receiver
- Emitter:
- Laser Diode (LD): Provides a focused, powerful beam for high accuracy (common in laser sensors). Can be Laser Class 1 or Class 2 (eye-safe).
- Transducer/Buzzer: Emits high-frequency ultrasonic waves (e.g., 40kHz) that are inaudible.
- IR LED: Emits infrared light (invisible) for short-range infrared sensors.
- Receiver:
- Photodiode/Phototransistor: Receives reflected light/laser beam.
- CMOS/CCD Array (Sensor Array): Used in Triangulation sensors. This array allows for precise determination of the angle/position of the reflected light spot.
- Transducer: A dual component that both emits and receives ultrasonic waves.
Signal Processing Circuit
This is the crucial block that determines the sensor’s accuracy and speed.
- Pulse Generator: Creates uniform pulses of waves or light.
- Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC): Converts the received voltage signal into digital data.
- Microcontroller/DSP: Executes complex algorithms:
- Calculates the precise Time of Flight (ToF) down to the nanosecond level.
- Performs noise filtering and temperature compensation algorithms (especially critical for ultrasonic sensors).
- Output Regulator: Converts the calculated distance value into an Analog 4-20mA/0-10V or Digital PNP/NPN signal.
Time of Flight (ToF) Measurement Principle
This principle is used by ultrasonic, laser, and long-range radar sensors for distance measurement:
- Pulse Emission: The sensor emits an energy pulse (Pulsed Laser or ultrasonic wave) at time t emit.
- Reflection Reception: The energy pulse hits the object and reflects back, being registered by the receiver at time t receive.
- Calculation: The distance (D) is calculated based on the travel time (Delta t = t receive – t emit) and the wave propagation speed (v):
Distance (D) = (v * Delta t) / 2
- Note: Speed (v) is the speed of sound (for ultrasonic) or the speed of light (c) (for laser). It must be divided by 2 because the signal travels two ways (out and back).
Triangulation Principle
This principle is applied to short-range optical or laser sensors, requiring very high accuracy:
- Light (Laser or IR LED) is emitted and projected onto the object.
- The reflected light is captured by a lens and focused onto a position sensor (CMOS/CCD Array).
- As the object moves closer or further away, the angle of reflection of the light beam changes, leading to a change in the position of the light spot on the Array.
- The microcontroller calculates the distance (D) based on the light spot position on the Array, the fixed distance between the Emitter and the Array, and other optical parameters (triangulation principle).
- Advantage: Extremely high resolution and accuracy, less affected by light intensity/object surface.
Classification of Distance Sensors and Their Pros & Cons
The classification of distance sensors is based on the type of energy they use for measurement.
Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
- Characteristics: Uses high-frequency sound waves (usually 40kHz-200kHz), operating on the ToF principle.
- Pros: Unaffected by color, transparency, or dust; can measure liquid levels and granular materials.
- Cons: Accuracy is significantly affected by changes in air temperature (as the speed of sound varies with temperature), average range (under 10m), and does not work well in a vacuum.
- Applications: Liquid/granular level measurement, car parking sensors, robot obstacle avoidance.
Laser Distance Sensor
This is the most versatile group of sensors, offering the best accuracy and measurement range.
| Laser Type | Principle | Characteristics | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Triangulation | Triangulation | Short-range (under 1m), extremely high resolution. | Very high (micrometer). |
| Laser Pulsed ToF | Time of Flight | Long-range (from 5m up to 300m), fast speed. | High (millimeter to cm). |
| LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) | ToF and Scanning | Creates a 3D map of the environment. | High (cm). |
- General Pros: High accuracy, long measurement range, fast response speed.
- Cons: Poor performance on transparent, dark matte (light-absorbing), or highly reflective (glare-inducing) surfaces.
Infrared (IR) Distance Sensor
- Principle: Primarily uses Triangulation or measures reflected light intensity.
- Characteristics: Very small size, low cost (common in consumer devices, IoT).
- Cons: Extremely short range (a few cm to 1m), low accuracy, and easily affected by ambient light and object color.
- Applications: Hobby robots (like HC-SR04 sensors), simple Arduino distance sensor projects.
Radar Distance Sensor
- Principle: Uses Radio Frequency (RF) waves, operating on the ToF principle. Often uses FMCW (Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave) Radar for high accuracy.
- Pros: Ability to penetrate non-metallic materials (plastic, glass, paper); performs extremely well in harsh weather conditions (rain, snow, dust, fog).
- Cons: Higher cost than laser, typically lower resolution than laser in ideal conditions.
- Applications: Heavy industry, level measurement in chemical tanks/silos, Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) systems in cars.
Advanced Technical Specifications and Selection Criteria
When choosing an industrial distance sensor, the following parameters are paramount:
Accuracy and Resolution
- Accuracy: The maximum deviation between the measured value and the actual value. Often expressed as an absolute value (e.g., +/- 0.5 mm) or a percentage of the full scale (e.g., 0.1% FS).
- Resolution: The smallest change in distance that the sensor can detect. For example, a sensor with a resolution of 0.01 mm can detect a positional change of only 10 micrometers.
- Repeatability: The sensor’s ability to provide the same measurement value when the object is repeatedly brought to the same position. This is the most crucial parameter for quality control applications.
Output Standard and Noise Immunity
- Analog (4-20mA): Current signal. The advantage is that it is less affected by electromagnetic interference and signal degradation over long cable distances, ideal for noisy industrial environments.
- Analog (0-10V): Voltage signal. Typically used in short-distance, low-noise applications.
- PNP/NPN (Digital): Used for ON/OFF state switching. PNP is used for positive-receiving PLCs/Systems, NPN for negative-receiving systems.
- RS485/IO-Link/Ethernet: Digital communication allows for high-speed and absolute reliable transmission of distance data, temperature, sensor status, and other diagnostic parameters.
Response Rate
- Measured in Hz (number of measurements per second) or kHz.
- If the object moves quickly (e.g., on a high-speed conveyor belt), a sensor with a high response rate (>= 1 kHz) is needed to avoid missing data.
- High-end Laser Triangulation sensors can achieve measurement speeds of up to 50 kHz.
Environmental Factors
- IP Rating: IP67 or IP69K is mandatory for environments involving washdown, dust, or temporary immersion.
- Operating Temperature: Ensure the sensor operates stably within the temperature range of the application.
- Ambient Light: For optical/laser sensors, resistance to glare from sunlight or factory lighting is important.
Comprehensive Applications of Distance Sensors
Distance sensors are the backbone of many industries and breakthrough technologies.
Specialized Industrial Applications
- Thickness and Dimension Measurement: High-precision Laser Triangulation sensors are used to measure the thickness of metal sheets, glass, or paper rolls in motion.
- Crane Positioning Control: Long-range Laser ToF is used to precisely locate overhead cranes or automated guided vehicles (AGV/AMR) in large warehouses.
- Tension Control: Measures the sag of cables or coiled material to maintain stable tension, preventing breakage or product deformation.
- Jam/Blockage Detection: Ultrasonic or laser sensors are used to monitor material flow on conveyors, alerting when material buildup exceeds acceptable levels.
Automotive and Transportation Applications
- ADAS (Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems):
- Radar: Provides distance, speed, and angle information for distant objects (Adaptive Cruise Control, Blind Spot Monitoring).
- LiDAR: Creates a high-precision 3D point cloud map of the vehicle’s surroundings, essential for Level 3 and above autonomous driving.
- Parking Sensors: Typically use ultrasonic sensors for short-range measurement when reversing/parking.
- Ship/Container Positioning: Long-range laser sensors are used to accurately position containers at automated ports.
Robotics and Smart Devices Applications
- Obstacle Avoidance Robots: Service robots, robotic vacuum cleaners, and AGVs use ultrasonic or infrared sensors to detect obstacles in the short range.
- Robotic Arms: Laser sensors are mounted on the robot gripper to precisely determine the position and tilt of the product before grasping (Pick and Place).
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV/Drone): Compact ToF sensors are used to measure altitude relative to the ground and assist safe landing.
Common Errors, Troubleshooting, and Installation Guide
Technical Notes for Installation
- Mounting Angle: Ideally, the sensor should be mounted perpendicular (90 degrees) to the target object’s surface to maximize the reflected signal. Avoid large oblique angles, especially for ultrasonic sensors.
- Reflective Surface:
- For Laser/Optical: If the object’s surface is too dark, increase sensitivity. If it is too glossy (mirror-like), slightly adjust the mounting angle to avoid direct light reflection.
- For Ultrasonic: Soft surfaces (like cotton wool, fabric) will absorb sound waves and reduce the effective measuring range.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Ensure signal cables are separated from AC power lines or other strong sources of electromagnetic interference. Use Shielded Cable for Analog signals.
Common Errors and Troubleshooting
| Error | Detailed Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No measurement/Max value | Object is outside the measuring range, surface absorbs all energy (dark matte), or sensor is obstructed. | Check the range, clean the sensor, or apply a reflector for laser sensors. |
| Large error/Signal jitter | Electromagnetic interference, temperature fluctuations (with ultrasonic), or mechanical vibration. | Use temperature compensation (if available), signal filters in the PLC, or isolate the sensor from vibration. |
| Poor linearity | Sensor has not been fully calibrated at the beginning and end points of the measuring range. | Perform 2-point calibration (Zero/Span Calibration). |
| Cannot detect transparent objects | Laser light passes through the object (e.g., glass, plastic bottles). | Use ultrasonic sensors, or specialized laser sensors designed for transparent objects. |
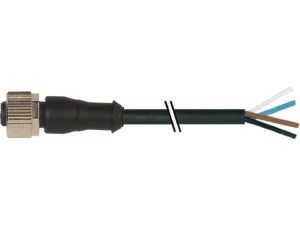
Basic Wiring Diagram (3 Wires)
- Power Wire V+: Typically Brown.
- Ground Wire GND: Typically Blue.
- Signal Wire OUT: Typically Black/White. This is where the Analog (4-20mA/0-10V) or Digital (PNP/NPN) signal connects to the PLC/Microcontroller.
Featured Distance Sensor Brands
Choosing a reputable manufacturer ensures performance and durability in harsh industrial environments:
- Baumer: Famous for its highly accurate laser sensors (OM series) and superior measurement speed, often trusted in precision automation.
- Keyence: Offers high-speed, ultra-small resolution laser and optical sensors for demanding quality control applications.
- Sick: A leader in optical, LiDAR, and Radar sensors, particularly strong in Logistics and autonomous robot solutions.
- Omron/Panasonic: Provides a wide range of products, from standard sensors to compact, highly reliable laser models.
- Autonics: Offers competitively priced products, suitable for standard applications and the Asian market.
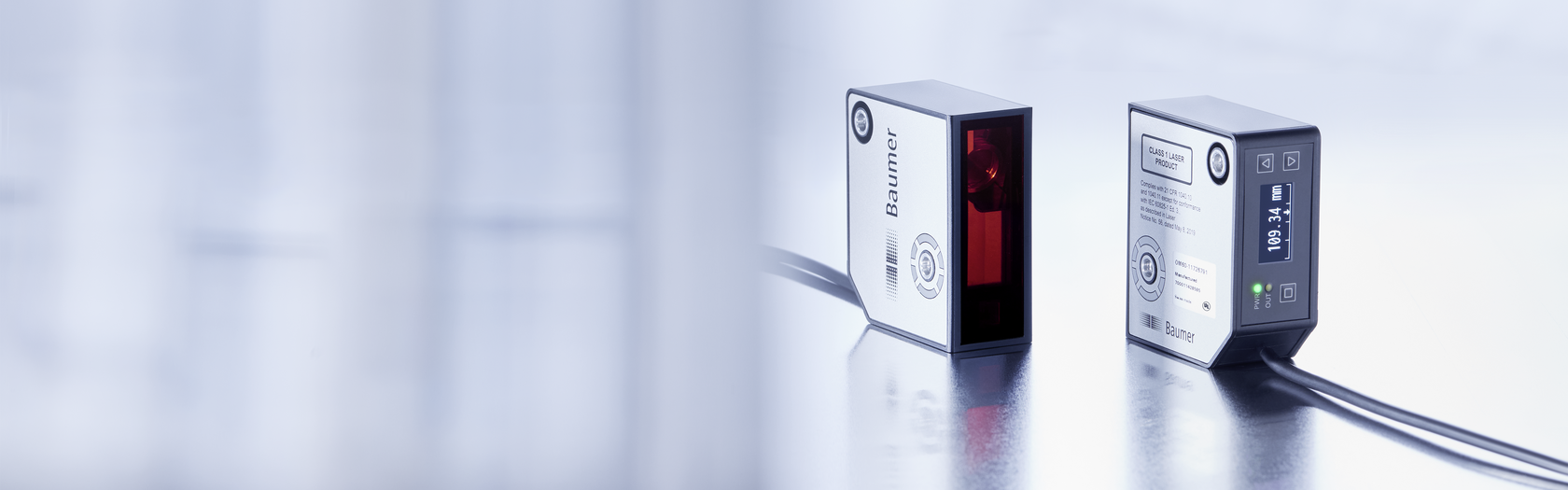
Product Highlight: Baumer’s OM60 Laser Distance Sensor
If you are looking for a top-tier laser distance sensor, Baumer’s OM60 is an excellent choice. This series is engineered for high performance, accuracy, and reliability, making them ideal for demanding applications in automation, robotics, and industrial measurement.
- Ultra-precise Measurement: Achieves accuracy up to +/- 3 µm and repeatability down to 0.12 µm.
- Long Measurement Range: Measures distances up to 1700 mm, even on dark or glossy surfaces.
- High-Speed Response: Fast update rates up to 5 kHz for real-time monitoring of moving objects.
- Surface Independent: Delivers consistent results across different materials and textures.
- User-Friendly Setup: Comes with an intuitive web interface or Baumer Sensor Tool for easy configuration.
- Flexible Connectivity: Supports modern protocols like IO-Link, serial, and Ethernet.
Whether you need precise component positioning, real-time quality control, or 3D surface measurement, Baumer’s laser distance sensors offer a complete and scalable solution.
Distance sensors are an indispensable part of the modern technology landscape, helping us achieve significant strides in automation, safety, and efficiency. Choosing the right type of sensor – whether it’s ultrasonic for simple applications, infrared for consumer devices, or laser (LiDAR) for superior accuracy and long range – will determine the success of your project and system.
With the detailed information on the operating principles, pros, cons, and applications of each type of distance sensor, we hope you have a clearer view to make an informed decision.
Product Suggestion: Baumer’s OM60 Laser Distance Sensor
If you are looking for a leading laser distance sensor, Baumer’s OM60 is the perfect choice. This sensor series is engineered for high performance, accuracy, and reliability, making them ideal for demanding applications in automation, robotics, and industrial measurement.
- Extremely Precise Measurement: Achieves accuracy up to $\pm 3\ \mu\text{m}$ and repeatability down to $0.12\ \mu\text{m}$.
- Long Measuring Range: Measures distances up to $1700\ \text{mm}$, even on dark or glossy surfaces.
- High-Speed Response: Fast update rate up to $5\ \text{kHz}$ for real-time monitoring of moving objects.
- Surface Independent: Provides consistent results across various materials and textures.
- User-Friendly Setup: Comes with an intuitive web interface or the Baumer Sensor Tool for easy configuration.
- Flexible Connectivity: Supports modern protocols such as IO-Link, serial, and Ethernet.
Whether you need precise part positioning, real-time quality control, or 3D surface measurement, Baumer’s laser distance sensors provide a complete and scalable solution.
Conclusion
Distance sensors are an indispensable part of the modern technological world, helping us achieve significant strides in automation, safety, and efficiency. Choosing the right type of sensor – whether it’s ultrasonic for simple applications, infrared for household devices, or laser (LiDAR) for superior accuracy and long range – will determine the success of your project and system.
With detailed information on the operating principles, pros, cons, and applications of each type of distance sensor, we hope you now have a clearer view to make an informed decision.

✅ Looking to learn more?
Join Baumer Live Webinar on July 15, 2025: “Precise Distance Measurement – Technologies, Applications & Innovations”. Get expert insights into sensing technologies—including radar, inductive, optical, and especially laser distance sensors—with real-world applications in quality control, dispensing, and wood processing.
Servo Dynamics Engineering: Authorized Distributor of Baumer in Vietnam
Servo Dynamics Engineering is the official authorized distributor of Baumer in Vietnam. We are committed to providing high-quality measurement and automation solutions.
We specialize in supplying Baumer’s most advanced laser distance sensor lines, including the OM60 series and industrial LiDAR solutions, ensuring absolute accuracy and reliability in high-speed positioning and dimension control applications.
If you are looking for an industrial distance sensor with superior accuracy and response speed, please contact us for in-depth technical consulting and optimal solutions for your automation system.
Explore Baumer Products
Learn more

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt