Consulting, Industrial Automation, Solutions
What is a Servo Drive? Structure, Working Principle, & Applications
The Servo Drive acts as the “brain” and amplifier, enabling automation systems to achieve absolute precision in position, speed, and torque control. In the era of Industry 4.0, the Servo Drive is an indispensable component in smart factories, high-speed CNC machines, and complex industrial robots.
This article provides a detailed explanation of what a Servo Drive is, its structure, working principles, common types, and guidance on selection and troubleshooting to ensure your system runs stably and efficiently.
What is a Servo Drive?

Servo Drive Concept
A Servo Drive, also known as a servo controller or servo amplifier, is an electronic power device that acts as an intermediary between the central controller (such as a PLC, CNC, or Motion Controller) and the Servo Motor.
The core function of the Servo Drive is to receive low-power control signals from the controller, then amplify and adjust the current, voltage, and frequency to drive the servo motor precisely according to the required parameters for position, speed, and torque.
Simply put, the Servo Drive is the “brain” and “power amplifier” for the servo motor, ensuring the motor operates accurately and efficiently.
Distinguishing Servo Drive, Servo Motor, and Servo System
| Term | Definition | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Servo Motor | An electric motor with a built-in feedback device (encoder/resolver). | Actuator (Muscle): Executes physical motion. |
| Servo Drive | An electronic power device that controls and powers the motor. | Controller (Brain/Amplifier): Receives commands, compares feedback, and adjusts electrical output. |
| Servo System | The complete combination of a Servo Drive, a Servo Motor, and a central controller (PLC/Motion Controller). | System (The Whole): Ensures precise closed-loop control according to requirements. |
What is a Servo Drive Used for? (Industrial Applications)
The main role of the Servo Drive is to ensure the motor accurately executes commands regarding:
- Position Control: Moving to a specific coordinate with micron-level accuracy.
- Speed Control: Maintaining a stable rotational speed or changing speed extremely quickly as required.
- Torque Control: Adjusting the tightening or pulling force to control the working process.
Advantages of Using Servo Drives Over Other Controllers
Servo Drives surpass Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) or Stepper Drives in the following aspects:
- High Precision: Closed-loop control ensures near-absolute elimination of position and speed errors.
- Fast Response: Extremely fast response capability, acceleration, and deceleration, ideal for short cycle times and continuously changing loads.
- Wide Speed Range: Maintains high torque even at low speeds or during startup.
Structure of a Servo Drive
A modern Servo Drive is typically composed of the following main components, ensuring efficient signal processing and power amplification.
Power Stage
The Power Stage is responsible for converting and supplying electrical energy to the motor:
- Rectifier: Converts the incoming AC power source into a DC source.
- DC Link: Contains large capacitors to smooth the DC voltage and store energy.
- Inverter: Uses high-power semiconductor components (like IGBTs, MOSFETs) to convert the filtered DC into a variable frequency AC source, supplying the motor.
Control Circuit
This is the “heart” of the Servo Drive, typically a high-speed Digital Signal Processor (DSP).
- Function: Processes PID control algorithms, compares the command signal (setpoint) with the feedback signal, and calculates the required current to be supplied to the motor.
- Processing Speed: Must be fast enough to execute control loops within microseconds, ensuring immediate response.
Feedback Unit (Feedback / Encoder Interface)
This circuit is responsible for communicating with the feedback device (Encoder or Resolver) mounted on the motor shaft.
- Function: Reads the pulses or absolute data regarding the motor’s current position and speed, then converts it into a digital signal to be sent back to the Control Circuit.
Communication Interface Module (EtherCAT, Ethernet/IP, Profinet…)
These communication ports allow the Servo Drive to receive commands from the PLC/Motion Controller and send back status data over an industrial network.
- Benefit: Synchronizes motion among multiple axes in complex automation systems.
Protection and Fault Monitoring System
This system continuously monitors operating parameters like current, voltage, and temperature. When an abnormality is detected, it shuts down power and signals a fault to protect both the Servo Drive and the motor.
Working Principle of a Servo Drive
The Servo Drive operates based on the principle of Closed-loop Control, which is the key factor enabling the precision of the servo system.
Closed-loop Control Principle
- Command Signal (Command): The high-level controller (PLC) sends a command request (e.g., “Move to position 5000 pulses”) to the Servo Drive.
- Actual Measurement (Feedback): The motor rotates, and the Encoder mounted on the motor shaft continuously measures the current position/speed and sends the feedback signal back to the Servo Drive.
- Error Calculation: The Servo Drive compares the Actual Position with the Required Position. Error = Command – Feedback.
- Correction: Based on the error, the control circuit calculates the necessary current to compensate for the deviation, then supplies that current via the Inverter to accelerate or decelerate the motor, bringing it back to the required position.
This process repeats continuously at an extremely high speed (often 1000 – 4000 times per second), ensuring minimal deviation.
Position – Speed – Torque Control
Most Servo Drives are capable of controlling three nested control loops:
- Torque Loop: The fastest, controlling the current supplied to the motor, thereby controlling the torque.
- Velocity Loop: The second fastest, controlling the motor’s rotational speed.
- Position Loop: The slowest (often controlled by the PLC), but the final objective, controlling the precise stopping position.
How the Servo Drive Communicates with the PLC / Motion Controller
The Servo Drive receives commands from the central controller through two primary forms:
- Pulse/Direction Signals: Suitable for simple, low-speed position control applications.
- Industrial Networks (Fieldbus): Uses protocols like EtherCAT, Profinet for high-speed transmission of position/speed commands and reception of feedback data, synchronizing multiple axes.
Processing Feedback Signals from the Encoder
The Servo Drive has specialized circuits to decode signals from Encoders (Incremental, Absolute, Sin/Cos) or Resolvers. This processing must ensure high accuracy and speed to provide instantaneous data for the control loop.
Comparing AC Servo vs. DC Servo Principles
| Criterion | AC Servo | DC Servo |
|---|---|---|
| Motor Type | Brushless motor, usually permanent magnet synchronous. | Brushed or Brushless motor. |
| Drive Structure | More complex (includes Rectifier, DC Link, 3-phase Inverter). | Simpler (mainly DC/DC power supply circuit or 1-phase Inverter). |
| Power Rating | Common in high power (from hundreds of Watts to tens of kW). | Common in low power (a few Watts to hundreds of Watts). |
| Applications | Heavy industry, robotics, CNC machines requiring high performance. | Medical devices, 3D printers, low-cost, low-power applications. |
Common Types of Servo Drives Today
AC Servo
The most common type in industrial settings, used to control brushless AC motors. They offer high torque and good energy efficiency, suitable for applications demanding high precision and speed.
DC Servo
Primarily used for brushed or brushless DC motors (BLDC). Often applied in low-power, low-voltage systems (e.g., battery-powered) or mobile devices.
Integrated Servo Drive
A type where the Servo Motor and Servo Drive are combined into a single unit. This saves space, reduces wiring, and simplifies installation. Often uses industrial network communication.
Distributed Servo Drive
The controller is placed near or directly on the motor, minimizing the length of power cables. Multiple distributed Drive units connect via a common communication network (e.g., EtherCAT).
Brushless – BLDC Servo Drives
A sub-category of AC/DC Servos, referring to Drives that control brushless motors. This is the modern standard due to high reliability and maintenance-free operation (no brushes).
Servo Drive Communication Protocols
The choice of communication protocol determines the speed and synchronization capability of the system.
EtherCAT
- Advantages: Extremely fast speed, real-time synchronization, ideal for multi-axis motion control and robotic systems.
Ethernet/IP
- Advantages: Seamless integration with Rockwell Automation (Allen-Bradley) and other major brands’ equipment, using standard Ethernet infrastructure. Suitable for large factory systems.
Profinet
- Advantages: Protocol developed by Siemens, popular in Europe. Offers real-time communication capabilities.
CANopen
- Advantages: Simple, low-cost, widely used in stand-alone machine applications with fewer axes.
When to Choose Which Protocol?
- Choose EtherCAT/Profinet: When high-speed and multi-axis synchronization is required (e.g., high-speed packaging machines, robots).
- Choose Ethernet/IP: When building systems with Rockwell/Allen-Bradley PLCs and equipment, or other suppliers supporting EIP.
- Choose CANopen: When a cost-effective solution is needed for single or low-axis machines.
Famous Servo Drive Brands in the Market
Choosing a reputable brand ensures quality, performance, and technical support services.
Rockwell (Allen-Bradley)
Offers Allen-Bradley Servo Drive lines deeply integrated into the Integrated Architecture platform, particularly strong with the EtherNet/IP protocol (e.g., Kinetix 5700, 5500).
Yaskawa Servo Drives
A Japanese brand famous for its Sigma Series (Sigma-7), highly regarded for its performance, reliability, and excellent control capability.
Mitsubishi
Popular with the MELSERVO line, offering diverse solutions from simple to complex, especially strong in the Asian market.
ABB
Provides integrated drive solutions, including high-performance Servo Drives, often used in heavy industrial applications and large power requirements.
Siemens
With the SINAMICS line, Siemens offers powerful controllers with Profinet integration, suitable for automation systems using Siemens PLCs.
Schneider
Offers integrated Motion Control solutions, often used in packaging and material handling machine solutions.
Applications of Servo Drives in Industry
Automated Production Lines
- Details: Controls repetitive movements, synchronizes conveyor speeds, feed mechanisms, and positioning devices in production lines.
Industrial Robots
- Details: Controls each joint of the robot arm, ensuring the robot moves to the required position with the highest accuracy (especially crucial in 6-axis robots).
CNC Machines, Cutting – Engraving – Milling Machines
- Details: Controls the linear and rotational motion of the X, Y, Z axes, ensuring the cutting tool follows the programmed path precisely, resulting in highly detailed products.
Packaging – Printing – Labeling
- Details: Synchronized speed control between film feeding, cutting, and heat sealing axes, requiring fast and high-precision response to keep up with packaging cycles.
High-Speed Synchronized Conveyors
- Details: Ensures all conveyors or drive components operate at the exact same speed, preventing misalignment or damage to products.
How to Choose the Right Servo Drive for Your System
Selecting a Servo Drive should be based on technical and economic factors to optimize performance.
Based on Power – Torque – Speed
This is the most critical criterion. You need to calculate:
- Load Inertia: To select a motor with suitable torque (often a 1:1 or 1:3 ratio with motor inertia).
- Maximum Speed: The motor and Drive must meet the highest rotational speed of the application.
- Required Power: Calculate the motor’s RMS (continuous) and Peak (instantaneous) power to select the corresponding Drive.
Based on Load Type & Drive Mechanism
- Heavy load, slow speed: May require a high-torque Drive/Motor.
- Light load, fast speed: Requires a low-inertia motor for quick acceleration/deceleration.
- Mechanism: Ball screws, gears, timing belts will affect the calculation of resolution (transmission ratio).
Based on Communication Protocol with PLC
Ensure the Servo Drive is compatible with your existing PLC or Motion Controller. For example:
- If using a Rockwell/Siemens PLC, prioritize Drives with EtherNet/IP or Profinet.
- If using a dedicated controller, EtherCAT is often the optimal choice.
Based on Operating Environment
- Temperature, Humidity: Choose a Drive with an appropriate IP rating (e.g., IP20 for control cabinets, IP65 for harsh environments).
- Installation Space: If space is limited, consider slim-type Drives or Integrated Servo Drives.
Based on Budget and Brand
- High Budget: Choose top brands (Rockwell, Yaskawa, Siemens) to ensure durability and advanced features.
- Limited Budget: Consider other brands with good performance but lower initial investment costs.
Common Servo Drive Faults & How to Fix Them
Understanding and promptly fixing faults helps minimize downtime.
Overcurrent, Overvoltage, and Overtemperature Faults
| Fault Type | Common Causes | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Overcurrent (OC) | Output short circuit, ground fault, excessively high control Gain. | Check motor cables, reduce Gain, check for mechanical faults causing motor blockage. |
| Overvoltage (OV) | Input voltage too high, motor decelerates too quickly (regenerative energy exceeds dissipation capacity). | Check power supply, install a Brake Resistor if necessary. |
| Overtemperature (OH) | Cooling fan failure, overload, high ambient temperature. | Clean/replace fan, install cabinet air conditioning, reduce motor load. |
Encoder / Feedback Signal Faults
- Causes: Broken encoder cable, loose connector, electromagnetic interference.
- Solution: Check the cable, ensure the cable is properly shielded and isolated from power cables.
Communication Faults (EtherCAT, Profinet…)
- Causes: Network configuration errors, damaged network cable, time synchronization errors (Jitter).
- Solution: Check IP/Node address, replace network cable, check controller response speed.
Signal Noise Faults in the Control Cabinet
- Causes: Signal and power cables running too close, incorrect grounding technique.
- Solution: Separate signal and power wiring, ensure all Drive and motor housings are grounded at a single common point.
Servo Drive Maintenance Guide
- Periodic Checks: Check cooling fans, capacitors (often have a limited lifespan), and tighten all wiring terminals.
- Environment: Ensure the control cabinet is sealed, clean, and maintains a stable temperature.
Summary: When Should You Use a Servo Drive?
Cases Requiring High Precision
If the application requires position accuracy below 1mm, especially at the micrometer level (e.g., SMT machines, optical measurement machines, CNC machines), the Servo Drive is the only choice.
Cases Requiring Fast Response
Applications with short duty cycles, continuous speed changes, rapid acceleration, and the need for immediate response (e.g., flying cut-off machines, high-speed packaging machines).
Cases Requiring Precise Force / Torque Control
When precise control of tightening force or tension is needed (e.g., winding/unwinding machines, assembly robots with force sensors), the Servo Drive provides flexible torque control capabilities.
FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions about Servo Drives
How is a Servo Drive different from a VFD?
| Criterion | Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) | Servo Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Speed control, energy saving. | Precise Position, Speed, Torque control. |
| Principle | Open loop or simple closed loop (Vector control). | Continuous closed loop with feedback from Encoder/Resolver. |
| Accuracy | Moderate, not suitable for positioning. | Very high, eliminating position errors. |
| Scope | Standard 3-phase AC asynchronous motors. | Dedicated Servo Motors with Encoders. |
Is an encoder mandatory for a Servo Drive?
Yes. An Encoder (or Resolver) is mandatory for the servo system to operate under the closed-loop principle. Without the feedback signal, the Servo Drive cannot know the motor’s actual position and will be unable to perform its precise control function.
How many axes can one Servo Drive control?
Typically, one Servo Drive controls only one axis (one motor). However, some modern Servo Drive lines (Multi-axis Drives) can integrate multiple Drive modules within a single chassis, but technically, each module still controls a separate axis.
What is the lifespan of a Servo Drive?
The typical lifespan of a Servo Drive is between 8 and 15 years, depending on environmental conditions and usage frequency. The key components determining the lifespan are the capacitors in the DC Link and the cooling fans. Regular maintenance can extend the equipment’s lifespan.
Can a Servo Drive be programmed?
Yes. Most Servo Drives can be programmed.
- Parameter Programming: Setting parameters such as Gain, Encoder resolution, speed/torque limits.
- Motion Programming (for smart Drives): Some Drives include integrated Motion Controller functions (Indexer Drives) that allow users to program simple motion profiles without an external Motion Controller.
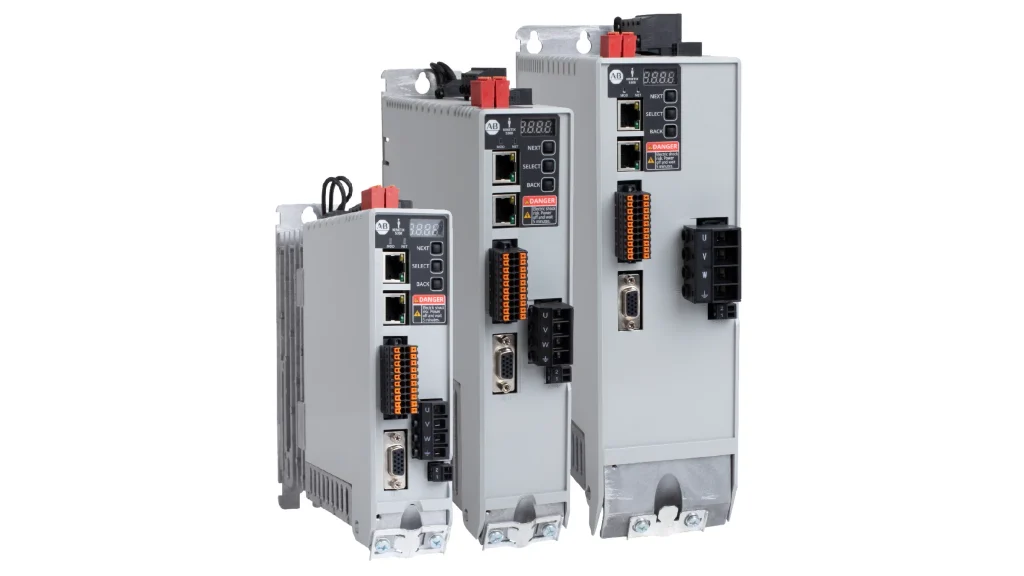
Allen-Bradley Servo Drives
Rockwell Automation offers a wide range of Allen-Bradley servo drive products, designed to meet diverse motion control needs in industrial applications. These drives integrate seamlessly with Rockwell’s automation ecosystem—including PLCs, programming software, and industrial networking solutions—simplifying the design, implementation, and operation of your automation systems.
Explore Allen-Bradley Servo Drive Product Lines
Servo Dynamics Engineering: Value-add Distributor for Rockwell Automation in Vietnam
If you are looking for high-performance motion control solutions, Servo Dynamics Engineering is your reliable partner. We are the official distributor of Rockwell Automation (Allen-Bradley) in Vietnam, specializing in providing genuine Allen-Bradley Kinetix Servo Drives, which integrate perfectly with your control system.
We provide not only products but also in-depth technical support, assisting you from design, motor/drive sizing, installation, to programming and operation, ensuring your automation system achieves optimal performance.
Contact Servo Dynamics immediately for expert consultation on Motion Control solutions.

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt